Setting up machine learning
Serverless Stack
To use the Elastic Stack machine learning features, you must have:
the appropriate subscription level or the free trial period activated
xpack.ml.enabledset to its default value oftrueon every node in the cluster (refer to Machine learning settings in Elasticsearch)mlvalue defined in the list ofnode.roleson the machine learning nodesmachine learning features visible in the Kibana space
security privileges assigned to the user that:
- grant use of machine learning features, and
- grant access to source and destination indices.
The fastest way to get started with machine learning features is to start a free 14-day trial of Elastic Cloud.
Assigning security privileges affects how users access machine learning features. Consider the two main categories:
- Elasticsearch API user: uses an Elasticsearch client, cURL, or Kibana Dev Tools to access machine learning features via Elasticsearch APIs. It requires Elasticsearch security privileges.
- Kibana user: uses the machine learning features in Kibana and does not use Dev Tools. It requires either Kibana feature privileges or Elasticsearch security privileges and is granted the most permissive combination of both. Kibana feature privileges are recommended if you control job level visibility via Spaces. Machine learning features must be visible in the relevant space. Refer to Feature visibility in Spaces for configuration information.
You can configure these privileges
- under the Roles and Spaces management pages. Find these pages in the main menu or use the global search field.
- via the respective Elasticsearch security APIs.
If you use machine learning APIs, you must have the following cluster and index privileges:
For full access:
machine_learning_adminbuilt-in role or the equivalent cluster privilegesreadandview_index_metadataon source indicesread,manage, andindexon destination indices (for data frame analytics analytics jobs only)
For read-only access:
machine_learning_userbuilt-in role or the equivalent cluster privilegesreadindex privileges on source indicesreadindex privileges on destination indices (for data frame analytics analytics jobs only)
The machine_learning_admin and machine_learning_user built-in roles give access to the results of all anomaly detection jobs, irrespective of whether the user has access to the source indices. You must carefully consider who is given these roles, as anomaly detection job results may propagate field values that contain sensitive information from the source indices to the results.
Granting All or Read Kibana feature privilege for Machine Learning will also grant the role the equivalent feature privileges to certain types of Kibana saved objects, namely index patterns, dashboards, saved searches, and visualizations as well as machine learning job, trained model and module saved objects.
In Kibana, the machine learning features must be visible in your space. To manage which features are visible in your space, go to the Spaces management page using the navigation menu or the global search field.
In addition to index privileges, source data views must also exist in the same space as your machine learning jobs. You can configure these under Data Views. To open Data Views, find Stack Management > Kibana in the main menu, or use the global search field.
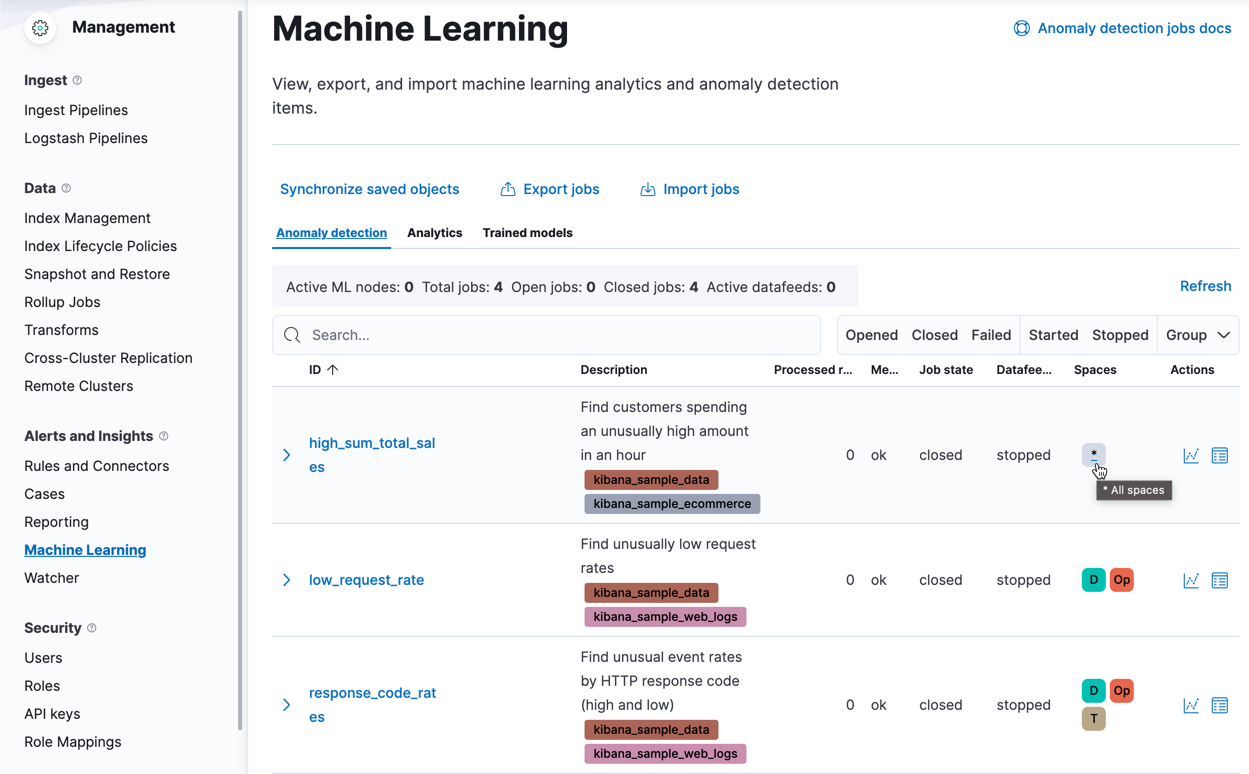
Each machine learning job and trained model can be assigned to all, one, or multiple spaces. This can be configured in Machine Learning. To open Machine Learning, find the page in the main menu, or use the global search field. You can edit the spaces that a job or model is assigned to by clicking the icons in the Spaces column.
Within a Kibana space, for full access to the machine learning features, you must have:
Machine Learning: AllKibana privilegesData Views Management: AllKibana feature privilegesread, andview_index_metadataindex privileges on your source indices- data views for your source indices
- data views,
read,manage, andindexindex privileges on destination indices (for data frame analytics analytics jobs only)
Within a Kibana space, for read-only access to the machine learning features, you must have:
Machine Learning: ReadKibana privileges- data views for your source indices
readindex privilege on your source indices- data views and
readindex privileges on destination indices (for data frame analytics analytics jobs only)
A user who has full or read-only access to machine learning features within a given Kibana space can view the results of all anomaly detection jobs that are visible in that space, even if they do not have access to the source indices of those jobs. You must carefully consider who is given access to machine learning features, as anomaly detection job results may propagate field values that contain sensitive information from the source indices to the results.
Data views can be automatically created when creating a data frame analytics analytics job.
For access to use machine learning APIs via Dev Tools in Kibana, set the Elasticsearch security privileges and grant access to machine_learning_admin or machine_learning_user built-in roles.
Within a Kibana space, to upload and import files in the Data Visualizer, you must have:
Machine Learning: ReadorDiscover: AllKibana feature privilegesData Views Management: AllKibana feature privilegesingest_adminbuilt-in role, ormanage_ingest_pipelinescluster privilegecreate,create_index,manageandreadindex privileges for destination indices
For more information, see Security privileges and Kibana privileges.
Export and import anomaly detection jobs and data frame analytics jobs to transfer them between clusters or environments, for example, from a test environment to production.
The exported files contain configuration details only; they do not contain the machine learning models.
- If your anomaly detection jobs use custom rules with filter lists, the filter lists must exist; otherwise, the import fails. To create filter lists, use Kibana or the create filters API
- If your anomaly detection jobs were associated with calendars, you must create the calendar in the new environment and add your imported jobs to the calendar. Use Kibana or the create calendars, add events to calendar, and add jobs to calendar APIs.
- To navigate to Anomaly detection jobs, use the global search field.
- Click Export jobs.
- Select the jobs, then click Export to download the job definition file.
- To navigate to Anomaly detection jobs, use the global search field.
- Click Import jobs.
- Upload the file that defines the anomaly detection job.
- Enter a job ID and click Import.
Anomaly detection jobs can be imported even if their data views or underlying indices are missing. In these cases, warnings are displayed, but the import is still allowed. Any issues raised by these warnings can be resolved later by adding the missing data views.
After importing an anomaly detection job, you must run it so that it can learn from your current data and build a model that reflects the new environment.
For data frame analytics, trained models are portable and can be transferred between clusters as described in Exporting and importing models.
- Data frame analytics jobs require their source index to exist before they can be imported. If the source index is missing, the import fails.
- To navigate to Data frame analytics, use the global search field.
- Click Export jobs.
- Select the jobs, then click Export to download the job definition file.
- To navigate to Data frame analytics, use the global search field.
- Click Import jobs.
- Select the file that defines the data frame analytics job.
- Enter a job ID and a destination index, then click Import.