Configure SSL/TLS for self-managed Fleet Servers
Stack
If you're running a self-managed cluster, configure Transport Layer Security (TLS) to encrypt traffic between Elastic Agents, Fleet Server, and other components in the Elastic Stack.
For comprehensive deployment information including all configuration flags, environment variables, and mTLS setup organized by connection type, refer to:
For the install settings specific to mutual TLS, as opposed to one-way TLS, refer to Elastic Agent deployment models with mutual TLS.
For a summary of flow by which TLS is established between components using either one-way or mutual TLS, refer to One-way and mutual TLS certifications flow.
Elastic Cloud provides secure, encrypted connections out of the box!
Configure security and generate certificates for the Elastic Stack. For more information about securing the Elastic Stack, refer to Configure security for the Elastic Stack.
Elastic Agents require a PEM-formatted CA certificate to send encrypted data to Elasticsearch. If you followed the steps in Configure security for the Elastic Stack, your certificate will be in a p12 file. To convert it, use OpenSSL:
openssl pkcs12 -in path.p12 -out cert.crt -clcerts -nokeys
openssl pkcs12 -in path.p12 -out private.key -nocerts -nodes
Key passwords are not currently supported.
When you run Elastic Agent with the Elastic Defend integration, the TLS certificates used to connect to Fleet Server and Elasticsearch need to be generated using RSA. For a full list of available algorithms to use when configuring TLS or mTLS, see Configure SSL/TLS for standalone Elastic Agents. These settings are available for both standalone and Fleet-managed Elastic Agent.
This section describes how to use the certutil tool provided by Elasticsearch, but you can use whatever process you typically use to generate PEM-formatted certificates.
Generate a certificate authority (CA). Skip this step if you want to use an existing CA.
./bin/elasticsearch-certutil ca --pemThis command creates a zip file that contains the CA certificate and key you’ll use to sign the Fleet Server certificate. Extract the zip file:
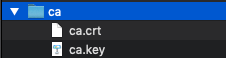
Store the files in a secure location.
Use the certificate authority to generate certificates for Fleet Server. For example:
./bin/elasticsearch-certutil cert \ --name fleet-server \ --ca-cert /path/to/ca/ca.crt \ --ca-key /path/to/ca/ca.key \ --dns your.host.name.here \ --ip 192.0.2.1 \ --pemWhere
dnsandipspecify the name and IP address of the Fleet Server. Run this command for each Fleet Server you plan to deploy.This command creates a zip file that includes a
.crtand.keyfile. Extract the zip file: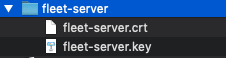
Store the files in a secure location. You’ll need these files later to encrypt traffic between Elastic Agents and Fleet Server.
Use the CLI to configure SSL or TLS when installing or enrolling Fleet Server. This method gives you granular control over certificate paths, verification modes, and authentication behavior.
For comprehensive information about all available CLI flags and environment variables organized by connection type, refer to How to deploy Fleet Server and How to deploy Elastic Agent.
Fleet Server needs a CA certificate or the CA fingerprint to connect securely to Elasticsearch. It also needs to expose a Fleet Server certificate so other Elastic Agents can connect to it securely.
For the steps in this section, imagine you have the following files:
ca.crt |
The CA certificate to use to connect to Fleet Server. This is the CA used to generate a certificate and key for Fleet Server. |
fleet-server.crt |
The certificate you generated for Fleet Server. |
fleet-server.key |
The private key you generated for Fleet Server. If the fleet-server.key file is encrypted with a passphrase, the passphrase will need to be specified through a file. |
elasticsearch-ca.crt |
The CA certificate to use to connect to Elasticsearch. This is the CA used to generate certs for Elasticsearch (see Prerequisites). The CA certificate's SHA-256 fingerprint (hash) may be used instead of the elasticsearch-ca.crt file for securing connections to Elasticsearch. |
To encrypt traffic between Elastic Agents, Fleet Server, and Elasticsearch:
Configure Fleet settings. These settings are applied to all Fleet-managed Elastic Agents.
In Kibana, open the main menu, then select Management > Fleet > Settings.
Under Fleet Server hosts, specify the URLs Elastic Agents will use to connect to Fleet Server. For example, https://192.0.2.1:8220, where 192.0.2.1 is the host IP where you will install Fleet Server.
TipFor host settings, use the
httpsprotocol. DNS-based names are also allowed.Under Outputs, search for the default output, then select the Edit icon in the Action column.
In the Hosts field, specify the Elasticsearch URLs where Elastic Agents will send data. For example, https://192.0.2.0:9200.
Specify either a CA certificate or CA fingerprint to connect securely Elasticsearch:
If you have a valid HEX encoded SHA-256 CA trusted fingerprint from root CA, specify it in the Elasticsearch CA trusted fingerprint field. To learn more, refer to the Elasticsearch security documentation.
Otherwise, under Advanced YAML configuration, set
ssl.certificate_authoritiesand specify the CA certificate to use to connect to Elasticsearch. You can specify a list of file paths (if the files are available), or embed a certificate directly in the YAML configuration. If you specify file paths, the certificates must be available on the hosts running the Elastic Agents.File path example:
ssl.certificate_authorities: ["/path/to/your/elasticsearch-ca.crt"]- The path to the CA certificate on the Elastic Agent host.
Pasted certificate example:
ssl: certificate_authorities: - | -----BEGIN CERTIFICATE----- MIIDSjCCAjKgAwIBAgIVAKlphSqJclcni3P83gVsirxzuDuwMA0GCSqGSIb3DQEB CwUAMDQxMjAwBgNVBAMTKUVsYXN0aWMgQ2VydGlmaWNhdGUgVG9vbCBBdXRvZ2Vu ZXJhdGVkIENBMB4XDTIxMDYxNzAxMzIyOVoXDTI0MDYxNjAxMzIyOVowNDEyMDAG A1UEAxMpRWxhc3RpYyBDZXJ0aWZpY2F0ZSBUb29sIEF1dG9nZW5lcmF0ZWQgQ0Ew ggEiMA0GCSqGSIb3DQEBAQUAA4IBDwAwggEKAoIBAQDOFgtVri7Msy2iR33nLrVO /M/6IyF72kFXup1E67TzetI22avOxNlq+HZTpZoWGV1I4RgxiQeN12FLuxxhd9nm rxfZEqpuIjvo6fvU9ifC03WjXg1opgdEb6JqH93RHKw0PYimxhQfFcwrKxFseHUx DeUNQgHkMQhDZgIfNgr9H/1X6qSU4h4LemyobKY3HDKY6pGsuBzsF4iOCtIitE9p sagiWR21l1gW/lNaEW2ICKhJXbaqbE/pis45/yyPI4Q1Jd1VqZv744ejnZJnpAx9 mYSE5RqssMeV6Wlmu1xWljOPeerOVIKUfHY38y8GZwk7TNYAMajratG2dj+v9eAV AgMBAAGjUzBRMB0GA1UdDgQWBBSCNCjkb66eVsIaa+AouwUsxU4b6zAfBgNVHSME GDAWgBSCNCjkb66eVsIaa+AouwUsxU4b6zAPBgNVHRMBAf8EBTADAQH/MA0GCSqG SIb3DQEBCwUAA4IBAQBVSbRObxPwYFk0nqF+THQDG/JfpAP/R6g+tagFIBkATLTu zeZ6oJggWNSfgcBviTpXc6i1AT3V3iqzq9KZ5rfm9ckeJmjBd9gAcyqaeF/YpWEb ZAtbxfgPLI3jK+Sn8S9fI/4djEUl6F/kARpq5ljYHt9BKlBDyL2sHymQcrDC3pTZ hEOM4cDbyKHgt/rjcNhPRn/q8g3dDhBdzjlNzaCNH/kmqWpot9AwmhhfPTcf1VRc gxdg0CTQvQvuceEvIYYYVGh/cIsIhV2AyiNBzV5jJw5ztQoVyWvdqn3B1YpMP8oK +nadUcactH4gbsX+oXRULNC7Cdd9bp2G7sQc+aZm -----END CERTIFICATE-----Install an Elastic Agent as a Fleet Server on the host and configure it to use TLS:
If you don’t already have a Fleet Server service token, select the Agents tab in Fleet and follow the instructions to generate the service token now.
TipThe in-product installation steps are incomplete. Before running the
installcommand, add the settings shown in the next step.From the directory where you extracted Fleet Server, run the
installcommand and specify the certificates to use.The following command installs Elastic Agent as a service, enrolls it in the Fleet Server policy, and starts the service.
sudo ./elastic-agent install \ --url=https://192.0.2.1:8220 \ --fleet-server-es=https://192.0.2.0:9200 \ --fleet-server-service-token=AAEBAWVsYXm0aWMvZmxlZXQtc2XydmVyL3Rva2VuLTE2MjM4OTAztDU1OTQ6dllfVW1mYnFTVjJwTC2ZQ0EtVnVZQQ \ --fleet-server-policy=fleet-server-policy \ --fleet-server-es-ca=/path/to/elasticsearch-ca.crt \ --certificate-authorities=/path/to/ca.crt \ --fleet-server-cert=/path/to/fleet-server.crt \ --fleet-server-cert-key=/path/to/fleet-server.key \ --fleet-server-port=8220 \ --elastic-agent-cert=/tmp/fleet-server.crt \ --elastic-agent-cert-key=/tmp/fleet-server.key \ --elastic-agent-cert-key-passphrase=/tmp/fleet-server/passphrase-file \ --fleet-server-es-cert=/tmp/fleet-server.crt \ --fleet-server-es-cert-key=/tmp/fleet-server.key \ --fleet-server-client-auth=requiredWhat happens if you enroll Fleet Server without specifying certificates? If the certificates are managed by your organization and installed at the system level, they will be used to encrypt traffic between Elastic Agents, Fleet Server, and Elasticsearch. If system-level certificates don’t exist, Fleet Server automatically generates self-signed certificates. Traffic between Fleet Server and Elastic Agents over HTTPS is encrypted, but the certificate chain cannot be verified. Any Elastic Agents enrolling in Fleet Server will need to pass the
--insecureflag to acknowledge that the certificate chain is not verified. Allowing Fleet Server to generate self-signed certificates is useful to get things running for development, but not recommended in a production environment.
Install your Elastic Agents and enroll them in Fleet.
Elastic Agents connecting to a secured Fleet Server need to pass in the CA certificate used by the Fleet Server. The CA certificate used by Elasticsearch is already specified in the agent policy because it’s set under Fleet settings in Kibana. You do not need to pass it on the command line.
The following command installs Elastic Agent as a service, enrolls it in the agent policy associated with the specified token, and starts the service.
sudo elastic-agent install --url=https://192.0.2.1:8220 \ --enrollment-token=<string> \ --certificate-authorities=/path/to/ca.crtDon't have an enrollment token? On the Agents tab in Fleet, select Add agent. Under Enroll and start the Elastic Agent, follow the in-product installation steps, making sure that you add the
--certificate-authoritiesoption before you run the command.
Stack
You can configure SSL/TLS settings for Fleet Server hosts directly in the Fleet UI, without relying on CLI flags or policy overrides.
To access these settings:
- In Kibana, go to Management > Fleet > Settings.
- Under Fleet Server hosts, select Add host or edit an existing host.
- Expand the SSL options section.
These are the available UI fields and their CLI equivalents:
The following table shows the available UI fields and their CLI equivalents:
| UI Field | CLI Flag | Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| Server SSL certificate authorities | --certificate-authorities |
CA to validate agent certificates (Fleet Server authenticates agent) |
| Client SSL certificate | --fleet-server-cert |
TLS certificate Fleet Server presents to agent (agent validates it) |
| Client SSL certificate key | --fleet-server-cert-key |
Key paired with the Fleet Server client certificate |
| Elasticsearch certificate authorities | --fleet-server-es-ca |
CA Fleet Server uses to validate Elasticsearch cert |
| SSL certificate for Elasticsearch | --fleet-server-es-cert |
Fleet Server’s mTLS certificate for Elasticsearch |
| SSL certificate key for Elasticsearch | --fleet-server-es-cert-key |
Key paired with the Fleet Server’s Elasticsearch certificate |
| Enable client authentication | --fleet-server-client-auth |
Require agents to present client certificates (mTLS only) |
Editing SSL or proxy settings for an existing Fleet Server might cause agents to lose connectivity. After changing client certificate settings, you might need to re-enroll the affected agents.
To configure a mutual TLS connection from Fleet Server to Elasticsearch, use the Elasticsearch output settings. For more information, refer to Output SSL options.