Downsampling concepts
This page explains core downsampling concepts.
Downsampling works with time series data streams only.
A time series is a sequence of observations taken over time for a specific entity. The observed samples can be represented as a continuous function, where the time series dimensions remain constant and the time series metrics change over time.
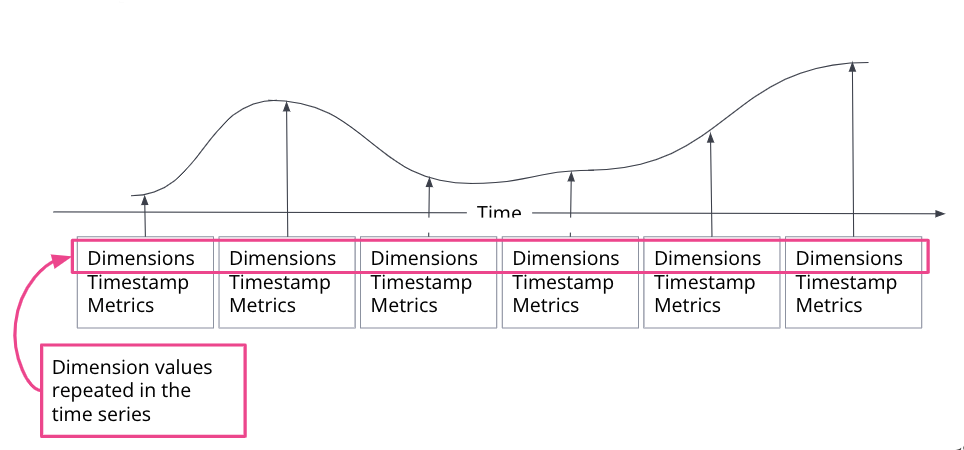
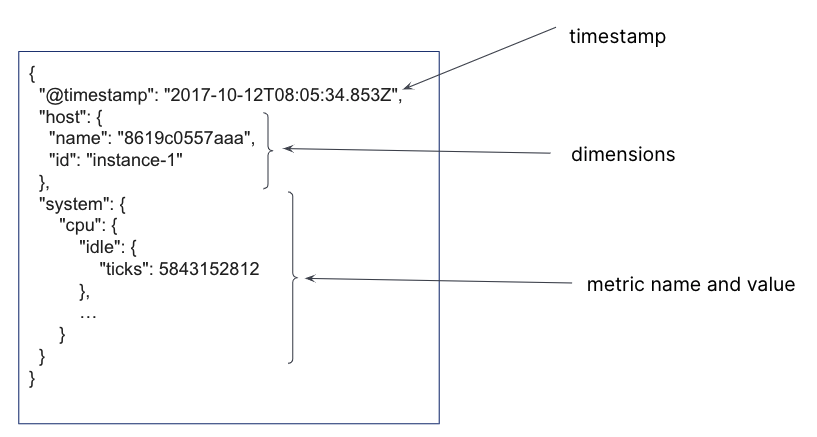
In a time series data stream, a single document is created for each timestamp. The document contains the immutable time series dimensions, plus metric names and values. Several time series dimensions and metrics can be stored for a single timestamp.
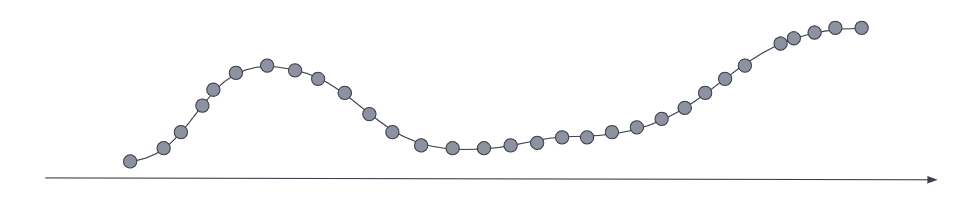
For the most current data, the metrics series typically has a low sampling time interval to optimize for queries that require a high data resolution.
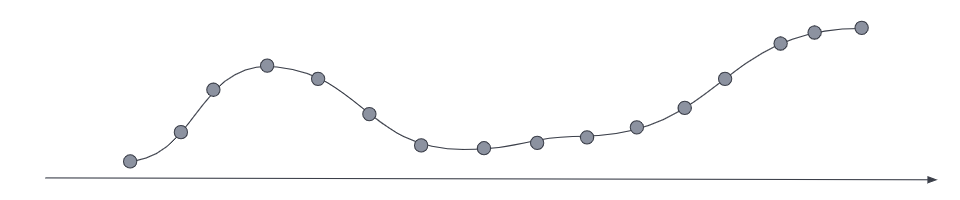
Downsampling reduces the footprint of older, less frequently accessed data by replacing the original time series with a data stream of a higher sampling interval, plus statistical representations of the data. For example, if the original metrics samples were taken every 10 seconds, you might choose to reduce the sample granularity to hourly as the data ages. Or you might choose to reduce the granularity of cold archival data to monthly or less.
Downsampling is applied to the individual backing indices of the TSDS. The downsampling operation traverses the source time series index and performs the following steps:
Creates a new document for each group of documents with matching
_tsidvalues (time series dimension fields), grouped into buckets that correspond to timestamps in a specific interval.For example, a TSDS index that contains metrics sampled every 10 seconds can be downsampled to an hourly index. All documents within a given hour interval are summarized and stored as a single document in the downsampled index.
For each new document, copies all time series dimensions from the source index to the target index. Dimensions in a TSDS are constant, so this step happens only once per bucket.
For each time series metric field, it computes the downsampled values based on the downsampling method.
For all other fields, copies the most recent value to the target index.
Replaces the original index with the downsampled index, then deletes the original index.
The new, downsampled index is created on the data tier of the original index and inherits the original settings, like number of shards and replicas.
You can downsample a downsampled index. The subsequent downsampling interval must be a multiple of the interval used in the preceding downsampling operation.
The downsampling method is the technique used to reduce multiple values within the same bucket into a single representative value. Two distinct methods exist:
last_value:This method increases the sampling interval by storing only the most recent value for each metric in the same bucket. While this reduces data accuracy, it offers the benefit of conserving storage space. It applies to all metric types. aggregate: This method preserves data accuracy by computing and storing statistical aggregations for all documents within the bucket, though it requires more storage space. It applies to each metric type in the following way:gaugefield type:min,max,sum, andvalue_countare stored as typeaggregate_metric_double.
counterfield type:- the last value is stored and the type is preserved.
histogramfield type:- individual histograms are merged into a single histogram that is stored, preserving the type. The
histogramfield type uses the T-Digest algorithm.
- individual histograms are merged into a single histogram that is stored, preserving the type. The
When downsampling a downsampled index, use the same downsampling method as the source index.
Fields in the target downsampled index are created with the same mapping as in the source index, with one exception: time_series_metric: gauge fields are changed to aggregate_metric_double.