Workflow tools
Workflows and Elastic Agent Builder are built to work together:
- Assign agents workflow tools to trigger workflows from your chats.
- Add
ai.agentsteps to invoke agents in your workflows.
Agents chat with your data by retrieving, summarizing, and reasoning. Workflows execute reliably with business-grade guardrails. Together, they combine flexible reasoning with deterministic execution.
Before using these features, ensure that:
- Workflows are set up: The feature must be enabled and you need specific privileges to create and run workflows. For details, see Set up workflows
- (Optional) If using the example below, ensure the Kibana sample flight data is installed.
Follow these steps to wrap an existing workflow into a tool that your agent can call. This is ideal for tasks that require a strict, repeatable sequence of actions.
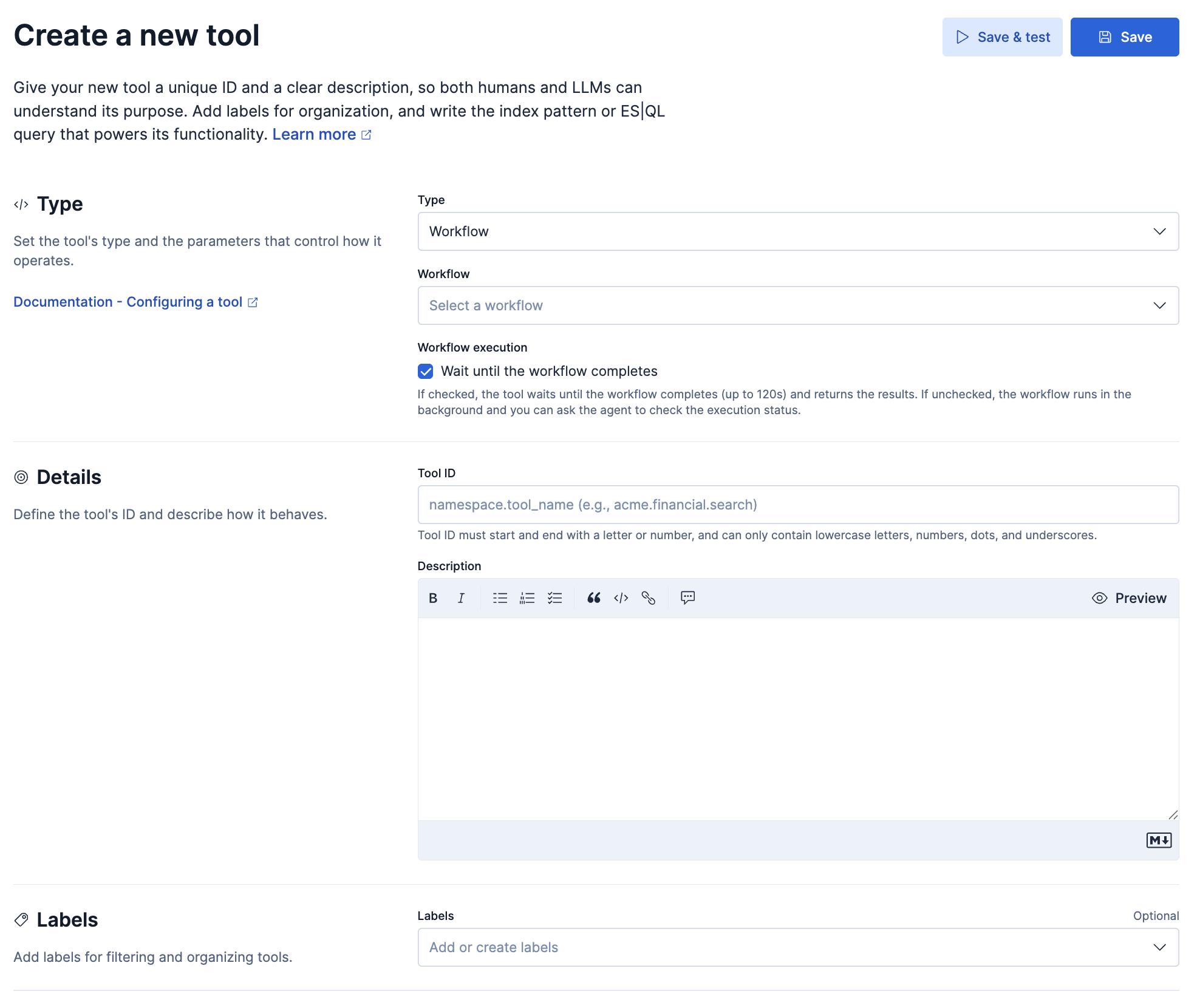
Navigate to Agents > More > View all tools > New tool.
Select Workflow as the tool type.
Select the specific workflow you want to wrap from the drop down list.
NoteThe UI will automatically detect the
inputsdefined in your workflow YAML and map them to tool parameters.Fill in the required fields:
- Tool ID: Create a unique identifier for the tool.
- Description: Ensure the description clearly explains when the agent should use this tool.
- Click Save.
Once you assign this tool to an agent, the agent can trigger the workflow autonomously.
- Navigate to Agents, select your agent, and click Add tool to assign the workflow tool you just created.
- Open the Agent chat and ask a question that triggers the workflow.
- The agent extracts the necessary parameters from the conversation, runs the workflow, and returns the workflow's final output to the chat.
Follow these steps to invoke an AI agent as a step within a workflow. This allows you to use the agent's reasoning capabilities to process data and return a summary.
- Open the Workflows editor and create or edit a workflow.
- Add a new step with the type
ai.agent. - Configure the step with the following parameters:
agent_id: The ID of the agent to call.message: The prompt to send to the agent.
The following example demonstrates a workflow that searches for flight delays and uses the Elastic AI Agent to summarize the impact.
version: "1"
name: analyze_flight_delays
description: Fetches delayed flights and uses an agent to summarize the impact.
enabled: true
triggers:
- type: manual
steps:
# Step 1: Get data from Elasticsearch
- name: get_delayed_flights
type: elasticsearch.search
with:
index: "kibana_sample_data_flights"
query:
range:
FlightDelayMin:
gt: 60
size: 5
# Step 2: Ask the agent to reason over the data
- name: summarize_delays
type: ai.agent
with:
agent_id: "elastic-ai-agent"
message: |
Review the following flight delay records and summarize which airlines are most affected and the average delay time:
{{ steps.get_delayed_flights.output }}
# Step 3: Print the agent's summary
- name: print_summary
type: console
with:
message: "{{ steps.summarize_delays.output }}"
- agent_id: The ID of the agent you want to call (must exist in Agent Builder).
- message: The prompt sent to the agent. You can use template variables (like
{{ steps.step_name.output }}) to inject data dynamically.
For advanced use cases, workflows can interact with Elastic Agent Builder programmatically using the generic kibana.request step. This allows you to perform management actions that aren't covered by the ai.agent step, such as listing available agents.
name: list_agents
enabled: true
triggers:
- type: manual
steps:
- name: list_agents
type: kibana.request
with:
method: GET
path: /api/agent_builder/agents