ES|QL tools in Elastic Agent Builder
ES|QL query tools enable you to create parameterized queries that execute directly against your Elasticsearch data. These custom tools provide precise control over data retrieval through templated ES|QL statements.
Use custom ES|QL tools when:
- You need precise control over the query logic
- Your use case involves repeatable analytical patterns
- You want to expose specific, parameterized queries to agents
- Results should be in a predictable tabular format
- You have well-defined data retrieval requirements
While agents can generate ES|QL queries dynamically using index search tools, custom ES|QL tools ensure syntax correctness and enforce critical business rules that an LLM might occasionally miss. For strategies to avoid data retrieval issues, refer to Context length exceeded.
- Execute pre-defined ES|QL queries with dynamic parameters
- Support typed parameters
- Return results in tabular format for structured data analysis
- Ideal for repeatable analytical queries with variable inputs
ES|QL tools support the following parameter types:
ES|QL tools support the following parameter types:
- String types:
text,keyword - Numeric types:
long,integer,double,float - Other types:
boolean,date,object,nested
ES|QL tools support the following parameter types:
- Textual types:
string - Numeric types:
integer,float - Other types:
boolean,date,array
Parameters can be configured as:
- Required: The agent must provide a value when calling the tool
- Optional: The agent can omit the parameter when calling the tool. You can set default values for optional parameters.
Optional parameters can have default values that are automatically applied when the agent doesn't provide a value. This ensures valid query syntax and consistent behavior.
When an agent calls a tool without specifying optional parameters, it automatically uses the defaults. When the agent provides a value, it overrides the default.
When creating ES|QL tools in the Kibana UI, you must specify default values for all optional parameters. This requirement ensures that tools have sensible fallback behavior and prevents configuration errors that could cause queries to fail at runtime.
When creating ES|QL tools via the API, default values for optional parameters are not required. However, they are strongly recommended to prevent query syntax errors when agents don't provide values. Without defaults, optional parameters that agents don't specify will be null, which can cause queries to fail.
For details about the ES|QL tools API, refer to the API documentation.
In your ES|QL query, reference parameters using the ?parameter_name syntax. The agent will automatically interpolate parameter values when executing the query.
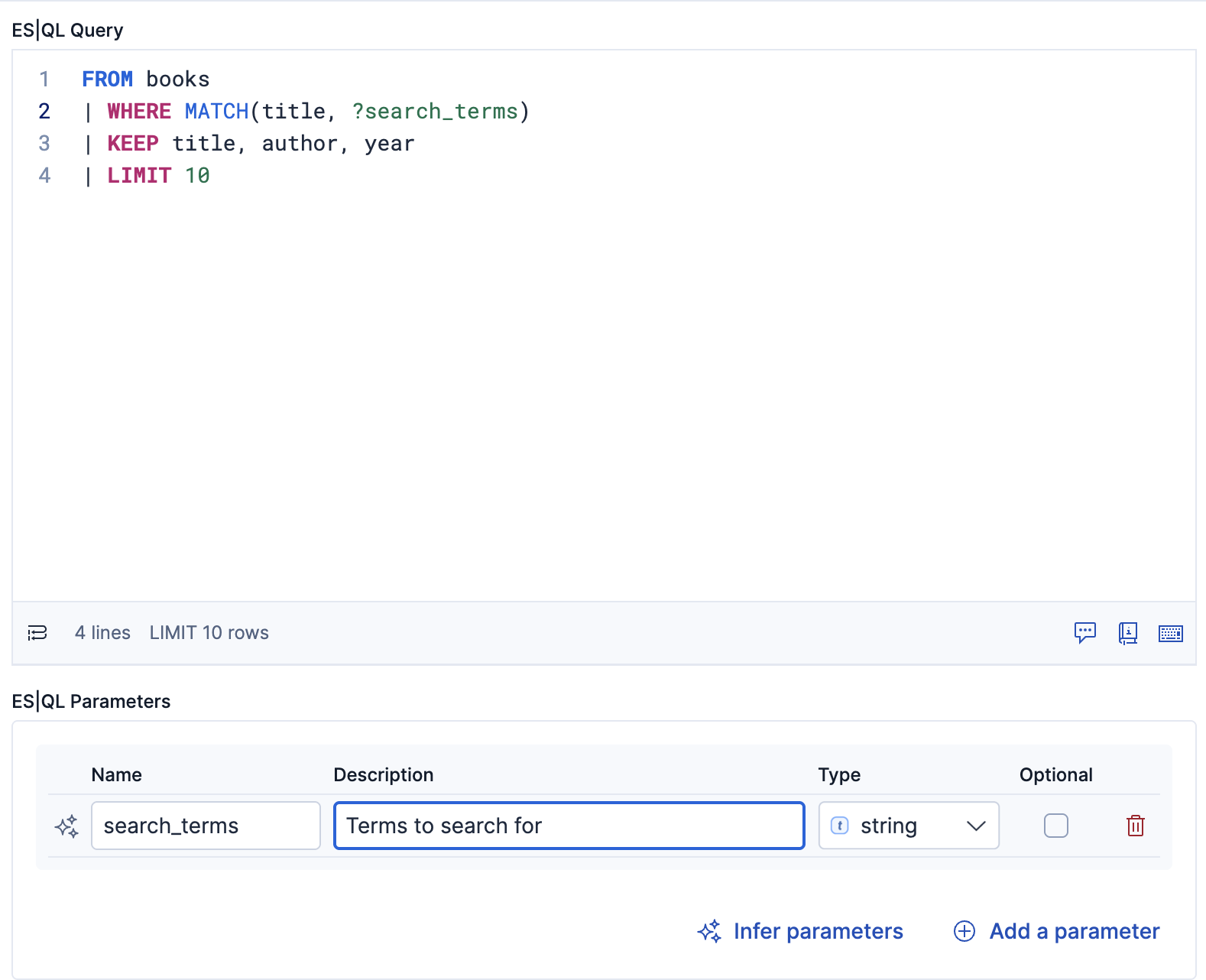
Here's an example ES|QL tool that searches for books using full-text search. ?search_terms is a named parameter that the agent will provide when executing the query.
FROM books
| WHERE MATCH(title, ?search_terms)
| KEEP title, author, year
| LIMIT 10
You can ask the LLM to infer the parameters for the query or add them manually.
For API examples, refer to Elastic Agent Builder Kibana APIs overview > Tools APIs
Complex analytical query example
For high-stakes or complex analytical queries, pre-defining the ES|QL logic guarantees correctness and enforces business rules.
Tool name: Calculate Quarterly Revenue
Description: "Calculates confirmed revenue for a specific region broken down by quarter. Input requires a region code (e.g., 'US', 'EU')."
Query:
FROM finance-orders-*
| WHERE order_status == "completed" AND region == ?region
| STATS total_revenue = SUM(amount) BY quarter
| LIMIT 5
- The
?regionparameter gives agents flexibility while keeping the core calculation logic consistent and reliable
- Include
LIMITclauses: Prevent returning excessive results by setting reasonable limits - Use meaningful parameter names: Choose names that clearly indicate what the parameter represents (for example,
start_dateinstead ofdate1) - Define parameter types: Ensure parameters have the correct type to avoid runtime errors
- Provide clear descriptions: Help agents understand when and how to use each parameter
- Use default values for optional parameters: Set sensible defaults for optional parameters to reduce complexity for agents and ensure consistent behavior when parameters are omitted
For general guidance on naming tools and writing effective descriptions, refer to Custom tools best practices.
If queries are slow or failing, you might be retrieving more data than the LLM can process. Refer to Context length exceeded for tips on diagnosing and resolving these issues.
ES|QL tools are subject to the current limitations of the ES|QL language itself. For more information, refer to ES|QL tool limitations.
To learn more about the language, refer to the ES|QL docs.