Build heat map charts with Kibana
Heat map charts display data as a grid of colored cells, where each cell's color represents the magnitude of a value. They are ideal for visualizing patterns across two categorical or temporal dimensions, identifying correlations, and spotting anomalies in large datasets.
You can create heat map charts in Kibana using Lens.
Before you start, make sure you have data indexed into Elasticsearch or install sample data. By default, Lens uses data views to access your Elasticsearch data. Data views are created automatically in most cases when you ingest data. You can also create one manually to select just the data that you want. Alternatively, you can use the ES|QL query mode to query your Elasticsearch data directly.
To build a heat map chart:
-
Access Lens
Lens is Kibana's main visualization editor. You can access it:
- From a dashboard: On the Dashboards page, open or create the dashboard where you want to add a heat map chart, then add a new visualization.
- From the Visualize library page by creating a new visualization.
-
Set the visualization to Heat map
New visualizations often start as Bar charts.
Using the Visualization type dropdown, select Heat map.
-
Define the data to show
- Select the data view that contains your data.
- Configure the Horizontal axis dimension to define the columns of the heat map.
- Configure the Cell value dimension to define the metric that determines cell colors.
Optionally:
- Configure the Vertical axis dimension to define the rows of the heat map. Without a vertical axis, the heat map displays a single row of colored cells.
The chart preview updates to show a grid of colored cells. Cell colors represent the magnitude of the metric value. If the grid appears empty, verify that the axes have data for the current time range.
-
Customize the chart to follow best practices
Tweak the appearance of the chart to your needs. Consider the following best practices:
- Choose appropriate dimensions
- Select dimensions that have a reasonable number of distinct values. Too many values create unreadable grids with tiny cells.
- Use sequential color palettes
- For data that ranges from low to high, use a sequential palette (light to dark). Reserve diverging palettes for data with a meaningful midpoint.
- Consider data density
- If cells are too small to read, reduce the number of buckets or use a larger time interval on your axes.
- Order categories meaningfully
- For categorical axes, order values logically (alphabetically, by frequency, or by a natural ordering like days of the week).
Refer to Heat map chart settings to find all configuration options for your heat map chart.
-
Save the chart
- If you accessed Lens from a dashboard, select Save and return to save the visualization and add it to that dashboard, or select Save to library to add the visualization to the Visualize library and reuse it later.
- If you accessed Lens from the Visualize library, select Save. A menu opens and offers you to add the visualization to a dashboard and to the Visualize library.
You can configure custom color ranges on the Cell value dimension to emphasize unusual values, making outliers immediately visible.
- Create a Heat map chart with your dimensions configured.
- Select the Cell value dimension to open its settings.
- In the Color palette configuration, select Custom to define your own color ranges:
- Normal range: Neutral colors (blues, grays)
- Anomalous range: Attention-grabbing colors (red, orange)
Customize your heat map chart to display exactly the information you need, formatted the way you want.
The Horizontal axis dimension defines the columns of the heat map.
- Data
-
The Horizontal axis dimension supports the following functions:
- Top values: Create columns for the most common values in a field.
- Field: Select the field to group by. You can add up to 4 fields to create multi-term columns. When multiple fields are selected, each column represents a unique combination of values across those fields. You can reorder the fields by dragging them to change their priority.
- Number of values: How many top values to display.
- Rank by: Specifies the dimension the top values are ranked by. Available options:
- Count of records: Rank by the number of documents containing each value. This is the default when a metric is defined.
- Alphabetical: Rank by the term key alphabetically. This is the default when no metric is defined.
- Rarity: Find terms that appear in very few documents, using a rare terms aggregation. You can configure the Max doc count to set the maximum number of documents a term can appear in to be considered rare (default: 1, max: 100). Only available for non-numeric fields and single-field terms.
- Significance: Find statistically unusual terms compared to the overall data set, using a significant terms aggregation. Only available for
keywordfields and single-field terms. - Custom: Define a custom metric aggregation to rank by (for example, rank by the sum of a numeric field rather than by count).
- Rank direction: Ascending or descending order. Disabled when Rank by is set to Rarity or Significance.
Advanced settingsSeveral advanced options allow you to refine the behavior of the breakdown:
- Include documents without the selected field: Off by default.
- Group remaining values as "Other": On by default.
- Enable accuracy mode: This option improves results for high-cardinality data, but increases the load on the Elasticsearch cluster.
- Include values: Values from the breakdown dimension to always show a tile for.
- Exclude values: Values from the breakdown dimension to always exclude from the displayed tiles.
- Date histogram: Group data into time-based buckets.
- Field: Select the date field to use for the time-based grouping.
Include empty rows: This option is on by default. Turn it off to exclude empty rows from the data.
Bind to global time picker: Associate the selected field to the Lens or dashboard main time selector.
Minimum interval: Define the time interval for aggregating the data. For example,
30s,20m,24h,2d,1w,1MDrop partial intervals: Exclude incomplete intervals from the data. This option is off by default.
- Intervals: Create numeric ranges for continuous data.
- Field: Select the numeric field to create intervals from.
- Include empty rows: Include intervals with no matching documents.
- Top values: Create columns for the most common values in a field.
- Appearance
-
- Name: Customize the axis label.
The Vertical axis dimension defines the rows of the heat map.
- Data
-
The Vertical axis dimension supports the same functions as the horizontal axis:
- Top values: Create rows for the most common values in a field.
- Field: Select the field to group by. You can add up to 4 fields to create multi-term rows. When multiple fields are selected, each row represents a unique combination of values across those fields. You can reorder the fields by dragging them to change their priority.
- Number of values: How many top values to display.
- Rank by: Specifies the dimension the top values are ranked by. Available options:
- Count of records: Rank by the number of documents containing each value. This is the default when a metric is defined.
- Alphabetical: Rank by the term key alphabetically. This is the default when no metric is defined.
- Rarity: Find terms that appear in very few documents, using a rare terms aggregation. You can configure the Max doc count to set the maximum number of documents a term can appear in to be considered rare (default: 1, max: 100). Only available for non-numeric fields and single-field terms.
- Significance: Find statistically unusual terms compared to the overall data set, using a significant terms aggregation. Only available for
keywordfields and single-field terms. - Custom: Define a custom metric aggregation to rank by (for example, rank by the sum of a numeric field rather than by count).
- Rank direction: Ascending or descending order. Disabled when Rank by is set to Rarity or Significance.
Advanced settingsSeveral advanced options allow you to refine the behavior of the breakdown:
- Include documents without the selected field: Off by default.
- Group remaining values as "Other": On by default.
- Enable accuracy mode: This option improves results for high-cardinality data, but increases the load on the Elasticsearch cluster.
- Include values: Values from the breakdown dimension to always show a tile for.
- Exclude values: Values from the breakdown dimension to always exclude from the displayed tiles.
- Date histogram: Group data into time-based buckets.
- Field: Select the date field to use for the time-based grouping.
Include empty rows: This option is on by default. Turn it off to exclude empty rows from the data.
Bind to global time picker: Associate the selected field to the Lens or dashboard main time selector.
Minimum interval: Define the time interval for aggregating the data. For example,
30s,20m,24h,2d,1w,1MDrop partial intervals: Exclude incomplete intervals from the data. This option is off by default.
- Intervals: Create numeric ranges for continuous data.
- Field: Select the numeric field to create intervals from.
- Include empty rows: Include intervals with no matching documents.
- Top values: Create rows for the most common values in a field.
- Appearance
-
- Name: Customize the axis label.
The Cell value dimension defines the metric that determines cell colors.
- Data
-
The value that determines cell color intensity. When you drag a field onto the chart, Kibana suggests a function based on the field type. You can use aggregation functions like
Sum,Average,Count,Median, and more, or create custom calculations with formulas.Advanced settingsDepending on the data you defined, several options allow you to apply additional filtering to the data taken into account to compute the final value to show.
Based on the type of visualization you're creating, only some of the following options can be available:
- Normalize by unit: Normalize the metric values to show per unit of time.
- Filter by: Specify a query.
- Reduced time range: Reduce the time range specified on the dashboard's time filter by the specified duration.
- Time shift: Shift the time range by the specified duration. This is useful if the value should use a different time range than the one selected on the dashboard.
- Hide zero values: Don't show values equal to zero. This option is on by default.
- Appearance
-
- Name: Customize the metric label displayed in tooltips.
- Value format: Control how numeric values are displayed (number, percent, bytes, and more).
- Color palette: Configure the color palette that maps cell values to colors. The default palette is Temperature. You can select a different palette, reverse the color direction, and define custom color ranges with specific value-to-color mappings.
When creating or editing a visualization, you can customize several appearance options from the
Style or Legend menus.
Titles and text
- Value labels
-
Control whether cell values are displayed as text inside each cell:
- Hide: Do not display values in cells (default).
- Show, if able: Display the metric value inside each cell when there is enough space. Cells that are too small to fit the text will not show a label.
Vertical axis
- Axis title
- Show or hide the vertical axis title. When visible, you can enter a custom title or use the default field name.
- Tick labels
- Toggle whether to show or hide the tick labels on the vertical axis.
Horizontal axis
- Axis title
- Show or hide the horizontal axis title. When visible, you can enter a custom title or use the default field name.
- Tick labels
- Toggle whether to show or hide the tick labels on the horizontal axis.
- Orientation
-
Control the orientation of horizontal axis tick labels. Only available when Tick labels is enabled.
- Horizontal: Labels are displayed horizontally (default).
- Vertical: Labels are rotated 90 degrees.
- Angled: Labels are displayed at a 45-degree angle.
- Visibility
-
Show or hide the legend:
- Show: Display the legend (default).
- Hide: Do not display the legend.
- Width
- Control the width of the legend panel. Options include Small, Medium, Large, and Extra large.
- Label truncation
- Toggle whether to truncate long legend labels. When enabled, set the Line limit to control the maximum number of lines for each label (defaults to 1).
The following examples show various configuration options for building impactful heat map charts.
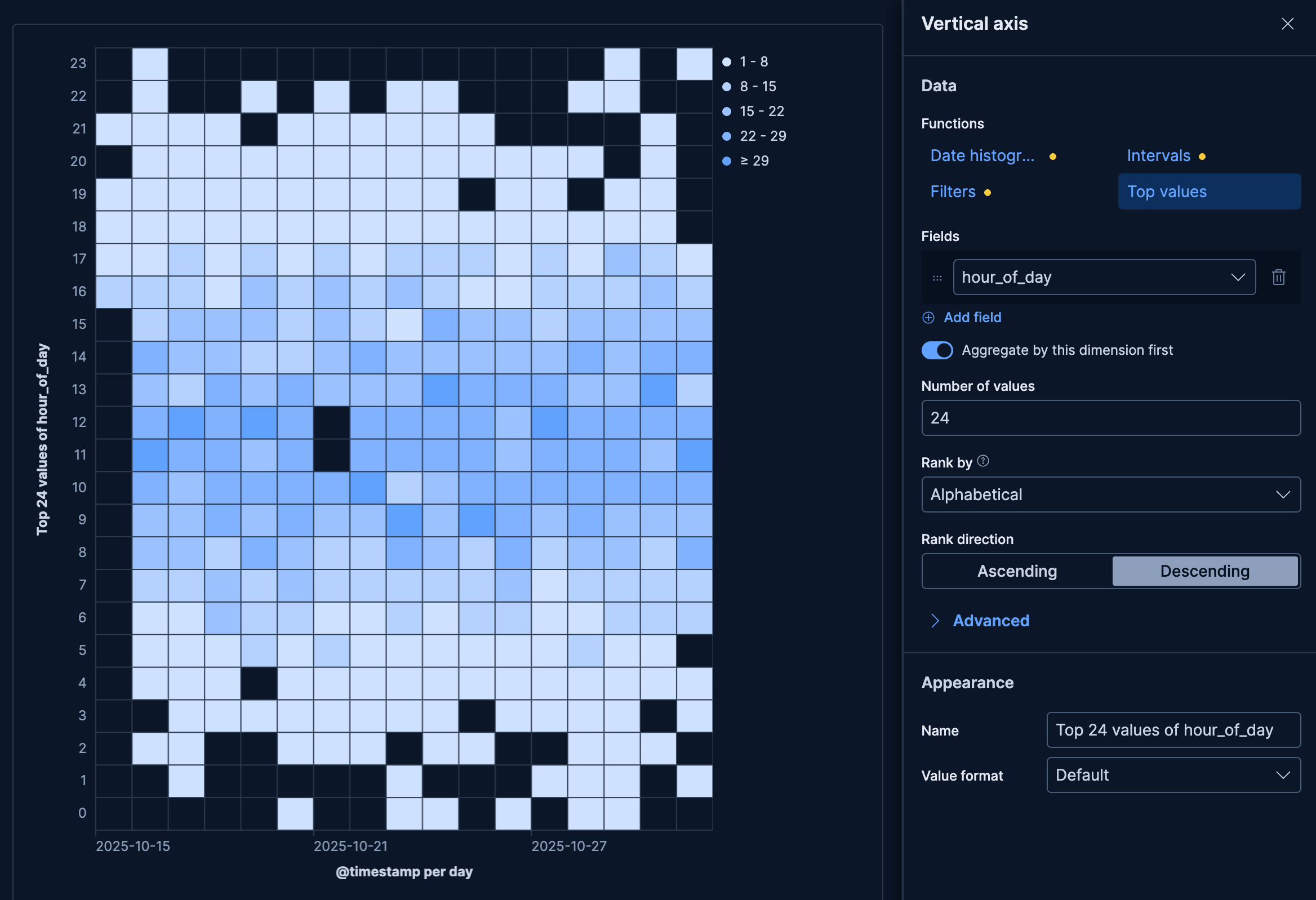
- Request volume by day and hour
-
Visualize when your website receives the most traffic using a runtime field that extracts the hour of the day (0-23) from
@timestamp:- Example based on: Kibana Sample Data Logs
- Horizontal axis:
@timestamp(Date histogram, daily) - Vertical axis:
hour_of_day(Top 24 values, "Aggregate by this dimension first" active, ranked by descending alphabetical order) - Cell value: Count
- Color palette: Cool (sequential)
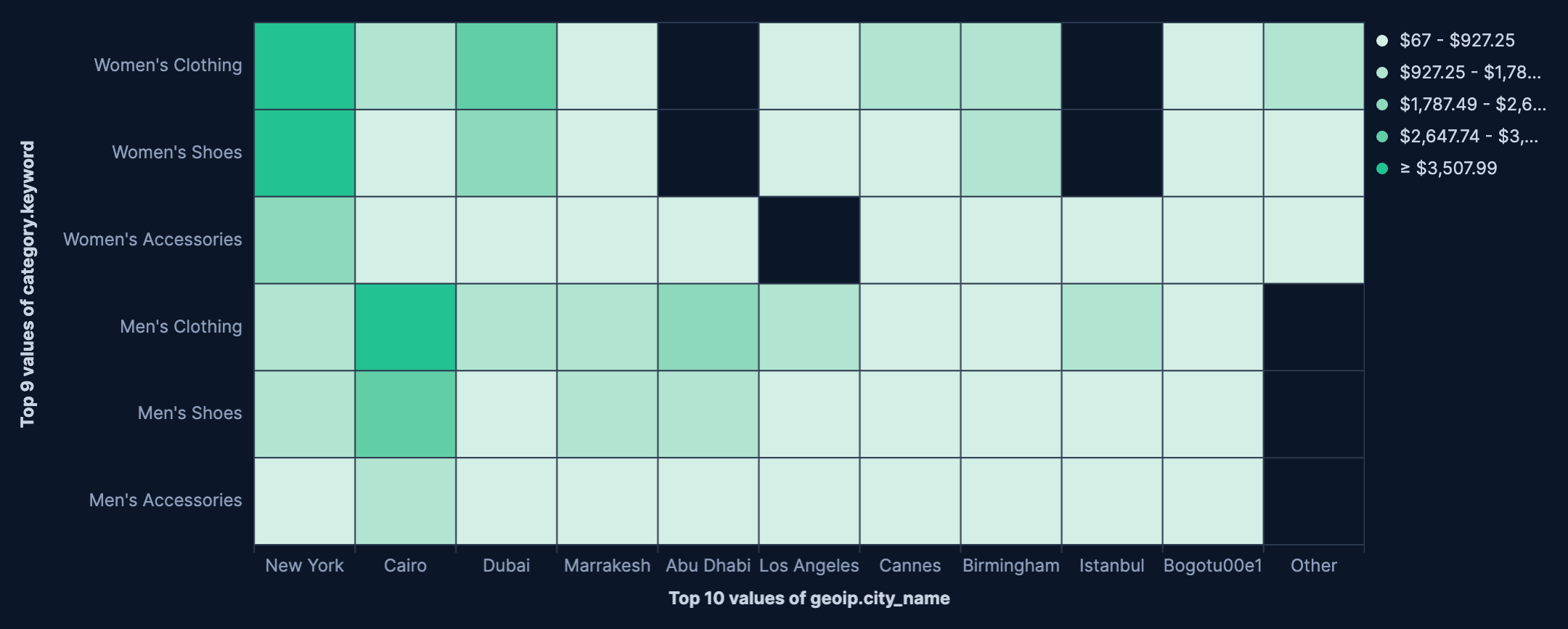
- Sales performance by product and region
-
Compare product sales across geographic regions:
- Example based on: Kibana Sample Data eCommerce
- Horizontal axis:
geoip.city_name(Top 10 values) - Vertical axis:
category.keyword(Top values) - Cell value:
Sum(taxful_total_price) - Color palette: Positive (sequential)