EDOT Cloud Forwarder for GCP
Serverless Observability ECH Self-Managed EDOT CF GCP
EDOT Cloud Forwarder (ECF) for GCP is a managed data pipeline that sends your Google Cloud logs to Elastic Observability. It uses Google Cloud Run and Pub/Sub under the hood to receive log events, process them with an OpenTelemetry Collector, and forward them to Elastic Cloud Managed OTLP Endpoint.
The architecture for the EDOT Cloud Forwarder GCP is as follows:
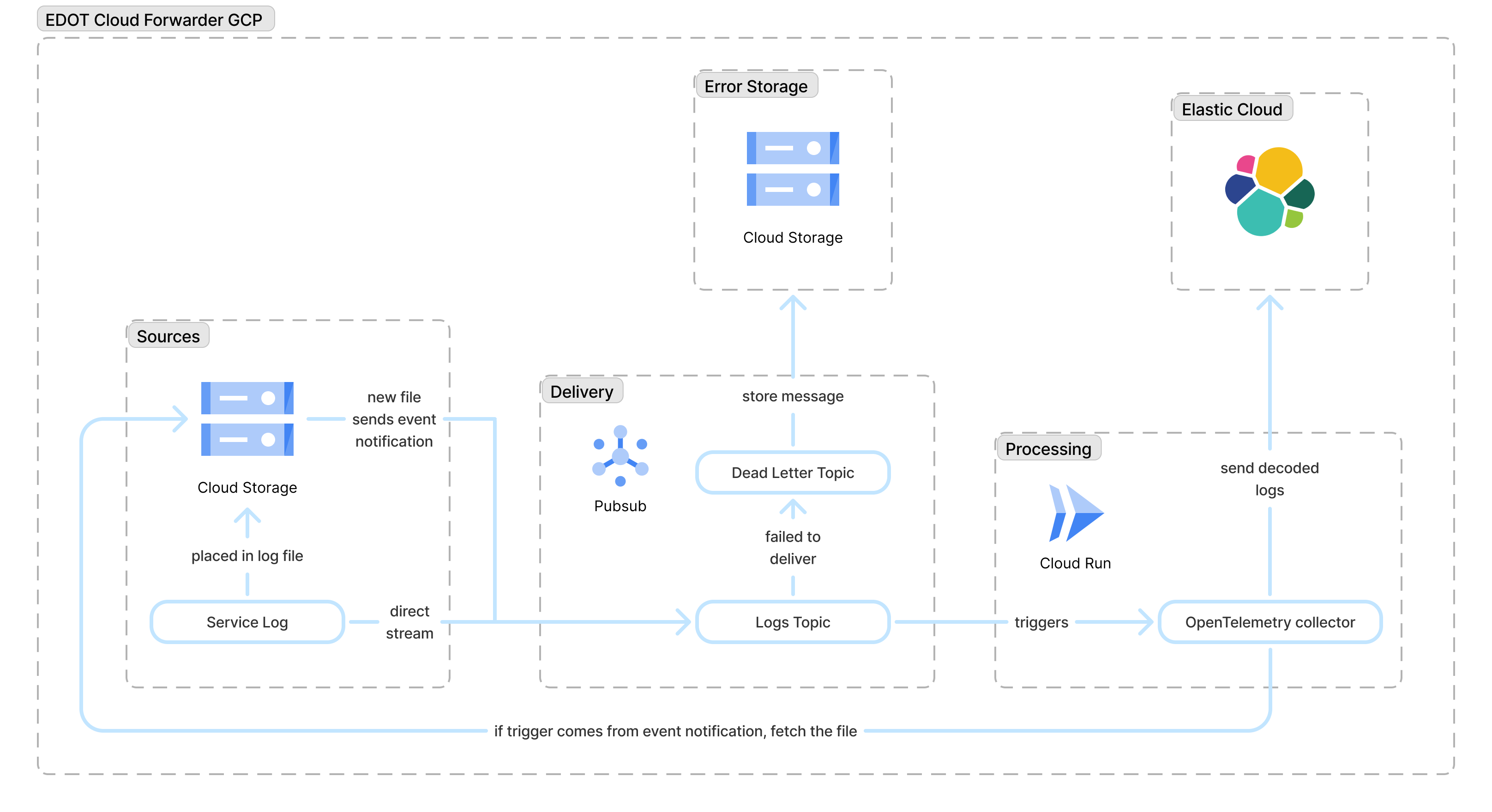
At a high level, the deployment consists of:
- A Pub/Sub topic and push subscription that receive log events from GCP services or GCS notifications.
- A Cloud Run service running the OpenTelemetry Collector, which transforms and forwards logs.
- An optional GCS bucket used as a landing zone for batch log files (for example, VPC Flow Logs).
- A dead-letter Pub/Sub topic and failure bucket that capture messages that could not be processed after retries.
- An Elastic Observability endpoint (Elastic Cloud Managed OTLP Endpoint) where all processed logs are finally stored and analyzed.
Data flows in the following way:
- Ingestion: Logs are sent to a Pub/Sub topic (either directly or using a GCS bucket notification).
- Processing: A push subscription triggers the Cloud Run service, where the OpenTelemetry Collector is running.
- Forwarding: The service processes the data and exports it to Elastic Cloud using the Elastic Cloud Managed OTLP Endpoint.
- Failure handling: If processing or forwarding still fails after retries, the failed messages are routed to a dead-letter topic and archived in a GCS bucket for future analysis.
Currently, EDOT Cloud Forwarder for GCP supports the following log types:
| Log | OTel mapping |
|---|---|
| Cloud Audit Log | Cloud Audit Log |
| VPC Flow Log | Access logs |
We are working to support other popular log types and sources. Contact us to let us know of any specific requirements that could influence our plans.
To collect logs using EDOT Cloud Forwarder for GCP, you need the following.
- Access to an Elastic Cloud Managed OTLP Endpoint.
- Valid API key with ingest permissions.
To retrieve your Elastic Cloud Managed OTLP Endpoint endpoint address and API key, follow these steps:
- In Elastic Cloud, create an Observability project or open an existing one.
- Go to Add data, select Applications and then select OpenTelemetry.
- Copy the endpoint and authentication headers values.
Alternatively, you can retrieve the endpoint from the Manage project page and create an API key manually from the API keys page.
Stack
- In Elastic Cloud, create an Elastic Cloud Hosted deployment or open an existing one.
- Go to Add data, select Applications and then select OpenTelemetry.
- Copy the endpoint and authentication headers values.
You need Terraform to deploy EDOT Cloud Forwarder for GCP. Follow the Terraform instructions to install it.
You can confirm it is correctly installed by running:
terraform --version
Make sure the following permissions are set in your Google Cloud project:
Project IAM Admin
The principal should be granted the built-in roles/resourcemanager.projectIamAdmin role, allowing them to manage IAM policies and roles at the project level.
Storage
The following permissions are needed for Cloud Storage management:
storage.buckets.createstorage.buckets.deletestorage.buckets.getstorage.buckets.getIamPolicystorage.buckets.setIamPolicystorage.buckets.update
Secret Manager
The following permissions are needed for Secret Manager management:
secretmanager.secrets.createsecretmanager.secrets.deletesecretmanager.secrets.getsecretmanager.secrets.getIamPolicysecretmanager.secrets.setIamPolicysecretmanager.secrets.updatesecretmanager.versions.accesssecretmanager.versions.addsecretmanager.versions.destroysecretmanager.versions.enablesecretmanager.versions.get
Pub/Sub
The following permissions are needed for Pub/Sub management:
pubsub.subscriptions.createpubsub.subscriptions.deletepubsub.subscriptions.getpubsub.subscriptions.getIamPolicypubsub.subscriptions.listpubsub.subscriptions.setIamPolicypubsub.subscriptions.updatepubsub.topics.attachSubscriptionpubsub.topics.createpubsub.topics.deletepubsub.topics.detachSubscriptionpubsub.topics.getpubsub.topics.getIamPolicypubsub.topics.setIamPolicypubsub.topics.update
Cloud Run
The following permissions are needed for Cloud Run management:
run.operations.getrun.services.createrun.services.deleterun.services.getrun.services.getIamPolicyrun.services.setIamPolicyrun.services.update
Service Account
The following permissions are needed for Service Account management:
iam.serviceAccountKeys.createiam.serviceAccountKeys.getiam.serviceAccounts.createiam.serviceAccounts.deleteiam.serviceAccounts.getiam.serviceAccounts.updateiam.serviceAccounts.actAs
Artifact Registry
The following permissions are needed:
artifactregistry.repositories.createartifactregistry.repositories.deleteartifactregistry.repositories.getartifactregistry.repositories.getIamPolicyartifactregistry.repositories.setIamPolicyartifactregistry.repositories.updateartifactregistry.repositories.downloadArtifacts
Follow these steps to get started with EDOT Cloud Forwarder for GCP.
-
Authenticate with GCP
You need to be authenticated on the Google project in which you want to deploy EDOT Cloud Forwarder for GCP. If you have
gcloudinstalled already, run this command:gcloud auth application-default loginOtherwise, follow Google instructions for the
gclouduse and configuration. -
Configure Terraform
Deploy EDOT Cloud Forwarder for GCP using the [Terraform module]((https://github.com/elastic/terraform-google-edot-cloud-forwarder).
First create a providers file,
providers.tf, then configure thegoogleprovider:provider "google" { project = "[GCP project]" region = "[GCP region]" }This ensures that you can deploy the Google resources on your project. Then create a new Terraform file,
main.tf, and add the EDOT Cloud Forwarder for GCP module:module "ecf" { source = "github.com/elastic/terraform-google-edot-cloud-forwarder?ref=v0.1.0" project = "[GCP project]" region = "[GCP region]" ecf_exporter_endpoint = "[Elastic Cloud Managed OTLP Endpoint]" ecf_exporter_api_key = "[Elastic Cloud Managed OTLP Endpoint API key]" }Refer to the EDOT Cloud Forwarder for GCP Terraform module for more details and advanced configuration.
NoteCurrently, the Terraform module can only be obtained using the EDOT Cloud Forwarder for GCP public repository. We are working on publishing it on the Terraform registry.
-
Deploy the module
Deploy the module using these Terraform commands:
terraform init terraform apply
The EDOT Cloud Forwarder is engineered for high-throughput, reliable ingestion, and simplified observability.
The EDOT Cloud Forwarder supports two primary event-driven ingestion patterns on GCP:
- Direct Pub/Sub: Ideal for logs streamed directly to a Pub/Sub topic by custom applications or other GCP services.
- GCS file notifications: Automatically ingests batch logs (like VPC Flow Logs or Audit Logs) placed in a file into a Google Cloud Storage bucket. The system listens for the
OBJECT_FINALIZEevent, reads the file content, and processes it.
Reliability is built-in to prevent data loss or infinite retry loops.
- Message acknowledgment: The service only acknowledges (ACKs) a Pub/Sub message upon successful forwarding to Elastic, ensuring that failed messages are automatically placed back in the queue for retry (or sent to the dead letter topic).
- Smart retries: The underlying Pub/Sub subscription is configured with exponential backoff. This prevents overwhelming the service with repeated failed messages during transient issues like network instability.
- Dead letter topic and failure bucket: If a message fails to be processed or forwarded after the configured maximum number of attempts, the EDOT Cloud Forwarder guarantees the message is sent to the dead letter topic. Messages sent to the dead letter topic are later archived in a dedicated GCS bucket. This prevents data loss and allows for later inspection.
EDOT Cloud Forwarder for GCP provides detailed context about its own health and the data it processes.
- Self-telemetry: You can enable the OpenTelemetry collector's internal metrics, allowing you to monitor the service's health.
- Metadata enrichment: By enabling the
include_metadataoption, logs are automatically enriched with context from the Pub/Sub and GCS transport layers, enabling better troubleshooting and correlation:bucketandobject, for logs coming from a GCS bucket.subscriptionandmessage_id.delivery_attempt, useful for tracking retries.
This section is still under active development. This guidance is an initial recommendation and might evolve as we refine sizing with Elastic Cloud Managed OTLP Endpoint.
Load tests were performed to understand how to run the ECF collector reliably in production. Tests were performed on a single Cloud Run service instance (1 vCPU) processing log files up to about 8MB in size (around 6,000 logs per file).
- Start with one ECF instance handling up to 10 concurrent requests. If you need to handle more traffic, add more instances rather than increasing concurrency on a single instance.
- Use at least 512MiB of memory per Cloud Run instance. In our tests at 10 concurrent requests, peak memory usage stayed below ~430MB, so 512MiB provides safe headroom for bursts.
- If your log files are significantly larger than 8MB, or you send many more logs per request, either lower the per‑instance concurrency, allocate more memory per instance, or do both to avoid out‑of‑memory issues.
- ECF forwards each log once. There should not be duplicate data under normal operation.
Retry behavior for permanent errors
The current retry logic treats all failures the same way, whether they're temporary (for example, a brief network issue) or permanent (such as an invalid log format). This means a message that can never be processed successfully will still go through all configured retries before it is finally sent to the dead‑letter topic and archived in the GCS bucket. While this improves resilience against transient failures, it can increase processing costs for messages that were never going to succeed.
Memory usage for large log files
ECF reads each log file fully into memory before sending it on. As a result, peak memory usage grows with both file size and the number of concurrent requests. Our recommendations (1 vCPU, 512MiB, up to 10 concurrent requests) are based on internal tests with files up to about 8MB (~6,000 logs) each. If you send much larger files or significantly more logs per request, you might need to lower per‑instance concurrency or allocate more memory per instance to avoid out‑of‑memory issues.
To remove EDOT Cloud Forwarder for GCP, destroy the resources created by Terraform by running this command:
terraform destroy