Isolate a host
Host isolation allows you to isolate hosts from your network, blocking communication with other hosts on your network until you release the host. Isolating a host is useful for responding to malicious activity or preventing potential attacks, as it prevents lateral movement across other hosts.
Isolated hosts, however, can still send data to Elasticsearch and Kibana. You can also create host isolation exceptions for specific IP addresses that isolated hosts are still allowed to communicate with, even when blocked from the rest of your network.
Host isolation is a Platinum or Enterprise subscription feature.
Hosts must have Elastic Agent installed with the Elastic Defend integration.
For Elastic Stack versions >= 7.15.0, host isolation is supported for endpoints running Windows, macOS, and these Linux distributions:
- CentOS/RHEL 8
- Debian 11
- Ubuntu 18.04, 20.04, and 22.04
- AWS Linux 2
To isolate and release hosts running any operating system, you must have the Host Isolation privilege.
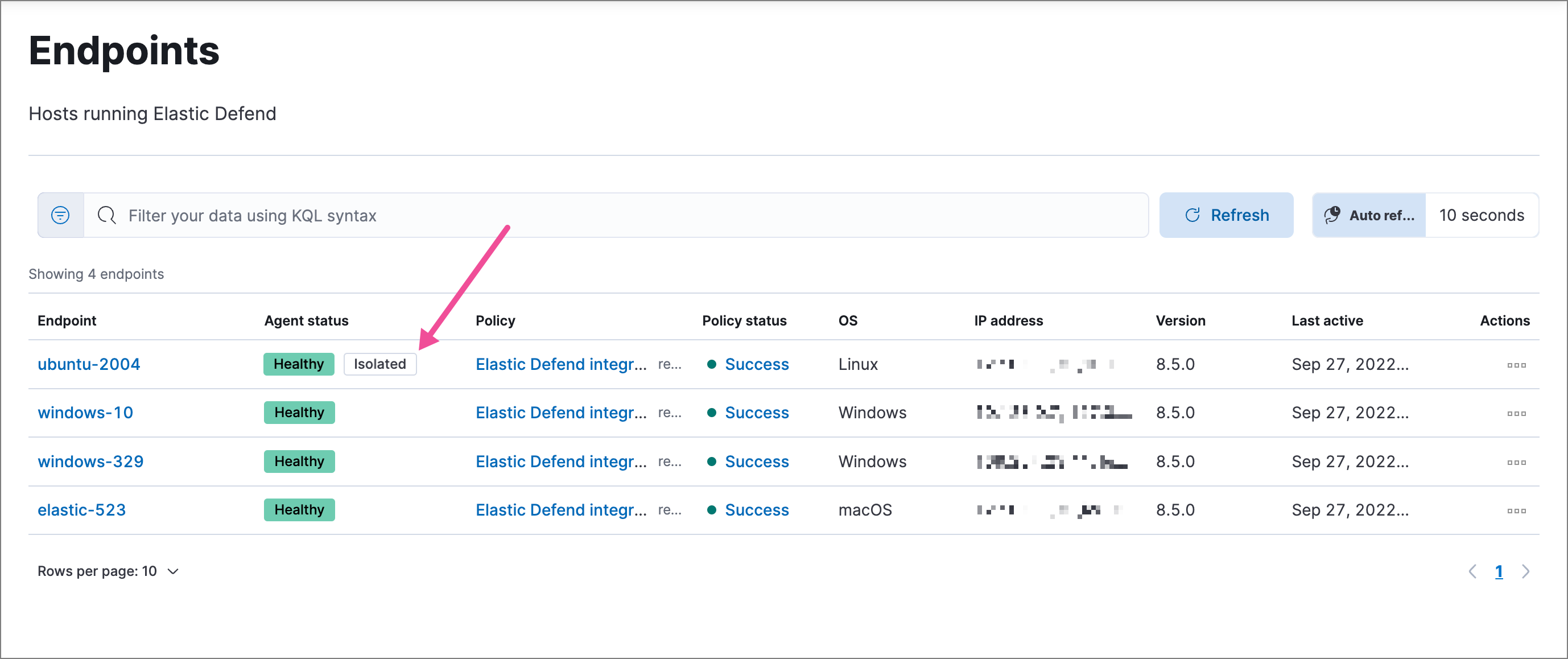
You can isolate a host from a detection alert’s details flyout, from the Endpoints page, or (with an Enterprise subscription) from the endpoint response console. Once a host is successfully isolated, an Isolated status displays next to the Agent status field, which you can view on the alert details flyout or Endpoints list table.
If the request fails, verify that the Elastic Agent and your endpoint are both online before trying again.
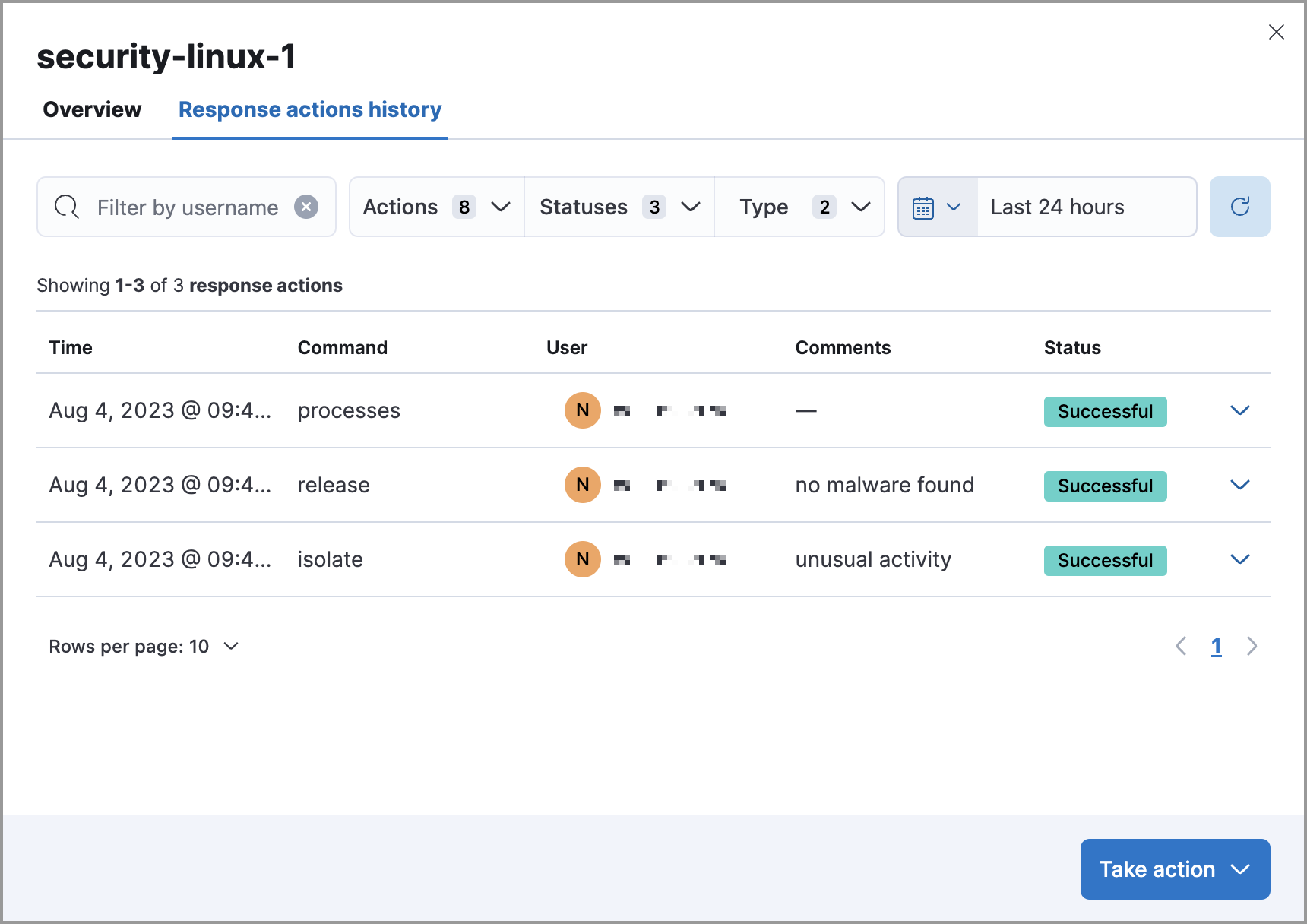
All actions executed on a host are tracked in the host’s response actions history, which you can access from the Endpoints page. Refer to View host isolation history for more information.
Isolate a host from a detection alert
Open a detection alert:
- From the Alerts table or Timeline: Click View details (
 ).
). - From a case with an attached alert: Click Show alert details (>).
- From the Alerts table or Timeline: Click View details (
Click Take action → Isolate host.
Enter a comment describing why you’re isolating the host (optional).
Click Confirm.
Isolate a host from an endpoint
Find Endpoints in the navigation menu or use the global search field, then either:
- Select the appropriate endpoint in the Endpoint column, and click Take action → Isolate host in the endpoint details flyout.
- Click the Actions menu (…) on the appropriate endpoint, then select Isolate host.
Enter a comment describing why you’re isolating the host (optional).
Click Confirm.
Isolate a host from the response console
The response console is an Enterprise subscription feature.
Open the response console for the host (select the Respond button or actions menu option on the host, endpoint, or alert details view).
Enter the
isolatecommand and an optional comment in the input area, for example:isolate --comment "Isolate this host"Press Return.
Automatically isolate a host using a rule’s endpoint response action
The host isolation endpoint response action is an Enterprise subscription feature.
Be aware that automatic host isolation can result in unintended consequences, such as disrupting legitimate user activities or blocking critical business processes.
Add an endpoint response action to a new or existing custom query rule. The endpoint response action will run whenever rule conditions are met:
- New rule: On the last step of custom query rule creation, go to the Response Actions section and select Elastic Defend.
- Existing rule: Edit the rule’s settings, then go to the Actions tab. In the tab, select Elastic Defend under the Response Actions section.
In the Response action field, select Isolate.
Enter a comment describing why you’re isolating the host (optional).
To finish adding the response action, click Create & enable rule (for a new rule) or Save changes (for existing rules).
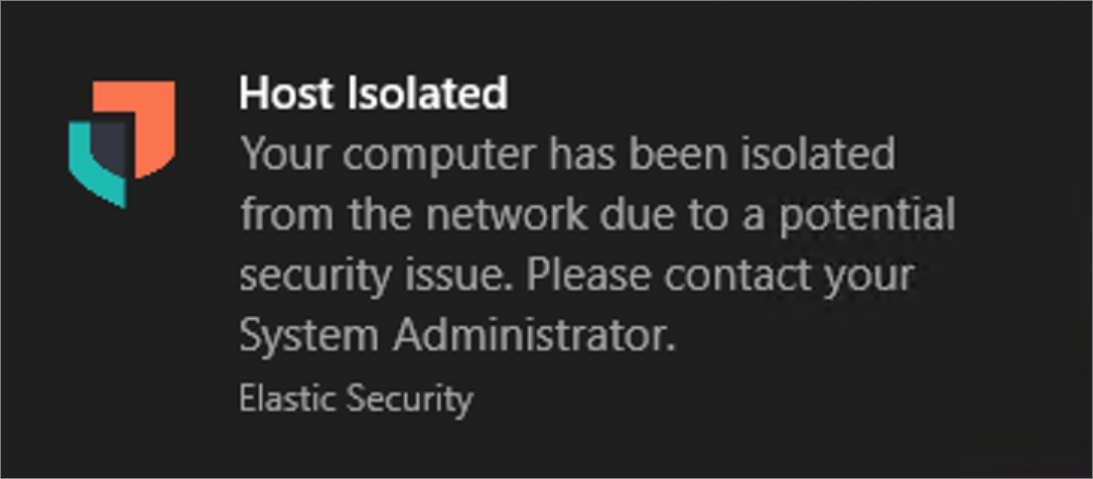
After the host is successfully isolated, an Isolated status is added to the endpoint. Active end users receive a notification that the computer has been isolated from the network:
Release a host from a detection alert
Open a detection alert:
- From the Alerts table or Timeline: Click View details (
 ).
). - From a case with an attached alert: Click Show alert details (>).
- From the Alerts table or Timeline: Click View details (
From the alert details flyout, click Take action → Release host.
Enter a comment describing why you’re releasing the host (optional).
Click Confirm.
Release a host from an endpoint
Find Endpoints in the navigation menu or use the global search field, then either:
- Select the appropriate endpoint in the Endpoint column, and click Take action → Release host in the endpoint details flyout.
- Click the Actions menu (…) on the appropriate endpoint, then select Release host.
Enter a comment describing why you’re releasing the host (optional).
Click Confirm.
Release a host from the response console
The response console is an Enterprise subscription feature.
Open the response console for the host (select the Respond button or actions menu option on the host, endpoint, or alert details view).
Enter the
releasecommand and an optional comment in the input area, for example:release --comment "Release this host"Press Return.
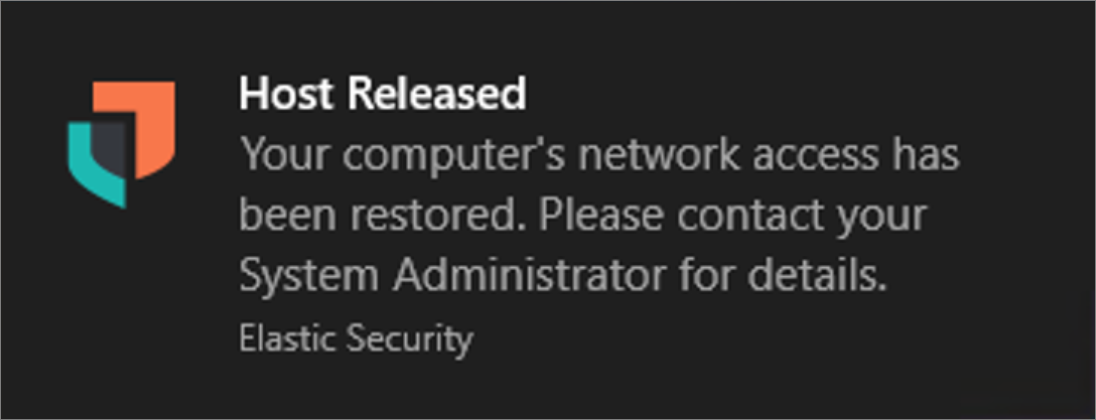
After the host is successfully released, the Isolated status is removed from the endpoint. Active end users receive a notification that the computer has been reconnected to the network:
To confirm if a host has been successfully isolated or released, check the response actions history, which logs the response actions performed on a host.
Go to the Endpoints page, click an endpoint’s name, then click the Response action history tab. You can filter the information displayed in this view. Refer to Response actions history for more details.