Saved objects
Elastic Stack Serverless
Kibana lets you save objects for your own future use or for sharing with others. Each saved object type has different abilities. For example, you can save your search queries made with Discover, which lets you:
- Share a link to your search
- Download the full search results in CSV form
- Start an aggregated visualization using the same search query
- Embed the Discover search results into a dashboard
For organization, every saved object can have a name, tags, and type. Use the global search to quickly open a saved object.
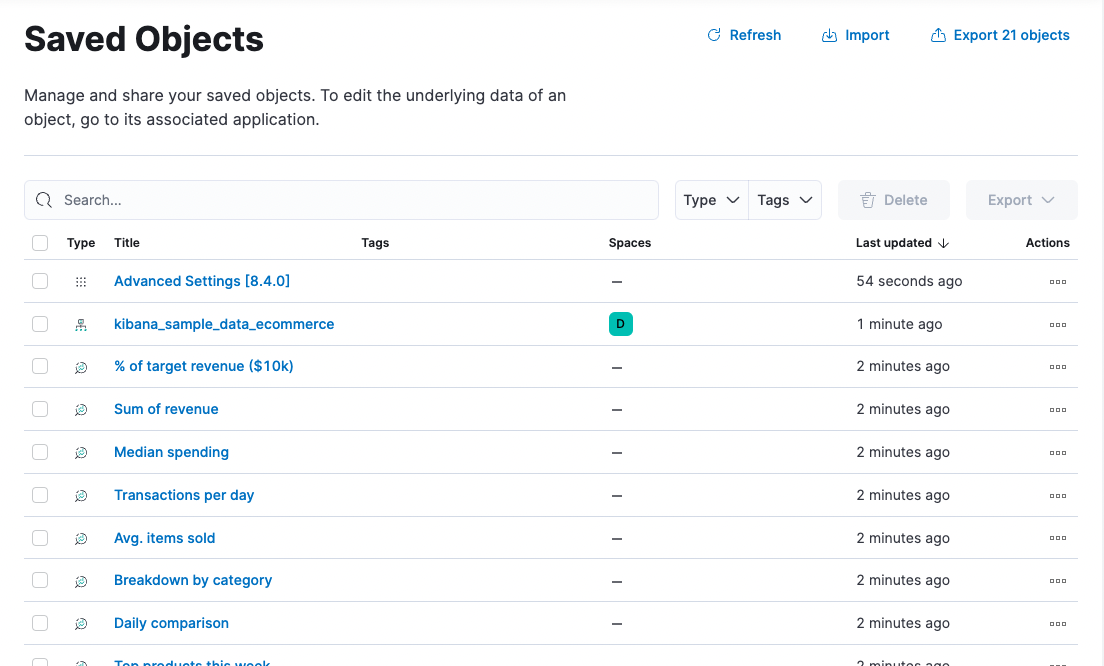
Edit, import, export, and copy your saved objects. These objects include dashboards, visualizations, maps, data views, Canvas workpads, and other saved objects.
You can find the Saved Objects page using the navigation menu or the global search field.
To access Saved Objects, you must have a role with the Saved Objects Management Kibana privilege.
Granting access to Saved Objects Management authorizes users to manage all saved objects in Kibana, including objects that are managed by applications they may not otherwise be authorized to access.
- To view and edit a saved object in its associated application, click the object title.
- To show objects that use this object, so you know the impact of deleting it, click the actions icon
and then select Relationships.
- To delete one or more objects, select their checkboxes, and then click Delete.
Use import and export to move objects between different Kibana instances. These actions are useful when you have multiple environments for development and production. Import and export also work well when you have a large number of objects to update and want to batch the process.
Kibana also provides import and export saved objects APIs for your Elastic Stack deployments and serverless projects to automate this process.
Import multiple objects in a single operation.
- In the toolbar, click Import.
- Select the NDJSON file that includes the objects you want to import.
- Select the import options. By default, saved objects already in Kibana are overwritten.
- Click Import.
The savedObjects.maxImportExportSize configuration setting limits the number of saved objects to include in the file. The savedObjects.maxImportPayloadBytes setting limits the overall size of the file that you can import.
Export objects by selection or type.
- To export specific objects, select them in the table, and then click Export.
- To export objects by type, click Export objects in the toolbar.
Kibana creates an NDJSON with all your saved objects. By default, the NDJSON includes child objects related to the saved objects. Exported dashboards include their associated data views.
The savedObjects.maxImportExportSize configuration setting limits the number of saved objects that you can export.
Copy saved objects and their related objects between spaces.
- Click the actions icon
.
- Click Copy to spaces.
- Specify whether to automatically overwrite any objects that already exist in the target spaces, or resolve them on a per-object basis.
- Select the spaces in which to copy the object.
The copy operation automatically includes child objects that are related to the saved object.
With each release, Kibana introduces changes to the way saved objects are stored. When importing a saved object, Kibana runs the necessary migrations to ensure that the imported saved objects are compatible with the current version.
However, saved objects can only be imported into the same version, a newer minor on the same major, or the next major. Exported saved objects are not backward compatible and cannot be imported into an older version of Kibana. For example:
| Exporting version | Importing version | Compatible? |
| 8.7.0 | 8.8.1 | Yes |
| 7.8.1 | 8.3.0 | Yes |
| 8.3.0 | 8.11.1 | Yes |
| 8.11.1 | 8.6.0 | No |
| 7.8.1 | 9.0.0 | No |
In the past, many saved object types could have the same ID in different spaces. For example, if you copied dashboard "123" from the one space to another space, the second dashboard would also have an ID of "123". While the saved object ID is not something that users would interact with directly, many aspects of Kibana rely on it, notably URLs. If you have a "deep link" URL to a saved dashboard, that URL includes the saved object ID.
Since version 8.0, Kibana requires most saved objects to have globally unique IDs. This is a change that we needed to make to support sharing saved objects to multiple spaces. Most saved objects cannot be shared to multiple spaces yet, but we needed to start enforcing globally unique object IDs first.
We have made several enhancements to minimize the impact, and this document describes what you need to know about the changes and how it will affect you.
Every time you upgrade Kibana, saved objects are migrated to a new format. When you first upgrade to version 8.x or later, this migration process will start enforcing globally unique saved object IDs.
In practical terms, any old saved objects that exist in a custom space will have their IDs changed to a new UUID, while saved objects in the Default space will be unchanged. This is how we can ensure that every saved object ID is unique. For example: if you had dashboard "123" in the Default space and dashboard "123" in Another space, after the upgrade you would have dashboard "123" in the Default space and dashboard "456" in Another space.
After you upgrade, or if you set up a new Kibana instance using version 8.x or later, there are a few more things that behave differently.
When you upgrade Kibana and saved object IDs change, the "deep link" URLs to access those saved objects will also change. To reduce the impact, each existing URL is preserved with a special legacy URL alias. This means that if you use a bookmark for a saved object ID that was changed, you’ll be redirected to the new URL for that saved object.
When you copy a saved object to another space, Kibana effectively exports it and imports it into that space. In this way, copying a saved object has always behaved like an import. In this document when we say "import", it applies to both features.
Historically, whether you imported or copied a saved object, Kibana would create at most one copy of a saved object in that space. If you imported the saved object multiple times, Kibana would overwrite the existing object, because it used the same ID. Since saved object IDs are now globally unique, Kibana maintains this functionality by tracking each saved object’s origin. When you import an object in version 8.x or later, Kibana uses either the saved object ID or the origin to determine its destination.
If you import a saved object using the "Check for existing objects" option, Kibana will take the following steps:
- If Kibana finds a matching saved object with the exact same ID in the target space, that will be the import destination — you can overwrite that destination or skip it.
- Otherwise, if Kibana finds a matching saved object with a different ID that has the same origin, that will be the import destination — again, you can overwrite that destination or skip it.
- Otherwise, if a saved object with the exact same ID exists in a different space, then Kibana will generate a random ID for the import destination, preserving the saved object’s origin.
- Otherwise, Kibana creates the saved object with the given ID.
For example, you have a saved object in an export.ndjson file, and you set up a brand new Kibana instance. You attempt to import the saved object using the "Check for existing objects" and "Automatically overwrite conflicts" options. The first time you import the saved object, Kibana will create a new object with the same ID (step 4 above). If you import it again, Kibana will find that object and overwrite it (step 1 above). If you then create a different space and import it there, Kibana will create a new object with a random ID (step 3 above). Finally, if you import it into the second space again, Kibana will find the second object with a matching origin and overwrite it (step 2 above).
When you import a saved object and it is created with a different ID, if 1. it contains weak links to other saved objects (such as a dashboard with a Markdown URL to navigate to another dashboard) and 2. the object’s ID has changed (step 3 above), those weak links will be broken. For more information, refer to the changelog.
If you are using the saved objects APIs directly, you should be aware of these changes:
Some of the saved objects APIs are deprecated since version 8.7.0. For more information, refer to the API docs
- When using the create or bulk create API, you may encounter conflict errors that cannot be overridden using the
overwrite: trueoption. This can occur if there is already a saved object with this ID in a different space, or if there is a legacy URL alias for this ID in the same space. - When using the import or copy to space API, objects can potentially be created with a different ID as described above.
- When using the delete API, if the saved object exists in multiple spaces, it can only be deleted by using the
forceoption.