Cloud deployment health and performance metrics
Elastic Cloud Enterprise and Elastic Cloud Hosted provide out of the box tools for monitoring the health of your deployment and resolving health issues when they arise.
These features augment AutoOps and stack monitoring features. These more complete monitoring features should be used if you plan to use your cluster in production.
Health is reported based on the following areas: Shard availability, master node health, Snapshot Lifecycle Management (SLM), Index Lifecycle Management (ILM), and repository integrity.
The deployment Monitoring page provides detailed information on health issues, impacted areas, and troubleshooting support.
To view the health for a deployment:
Log in to the Elastic Cloud Console or ECE Cloud UI.
On the home page, find your deployment.
TipIf you have many deployments, you can instead go to the Hosted deployments (Elastic Cloud Hosted) or Deployments (Elastic Cloud Enterprise) page. On that page, you can narrow your deployments by name, ID, or choose from several other filters.
Select Manage.
- From the navigation menu, select Monitoring.
The Monitoring page provides the following information:
- Health issues for Kibana, Enterprise Search, APM, and plan changes are reported in the health banner.
- Health issues for Elasticsearch clusters are broken down into a table with more details.
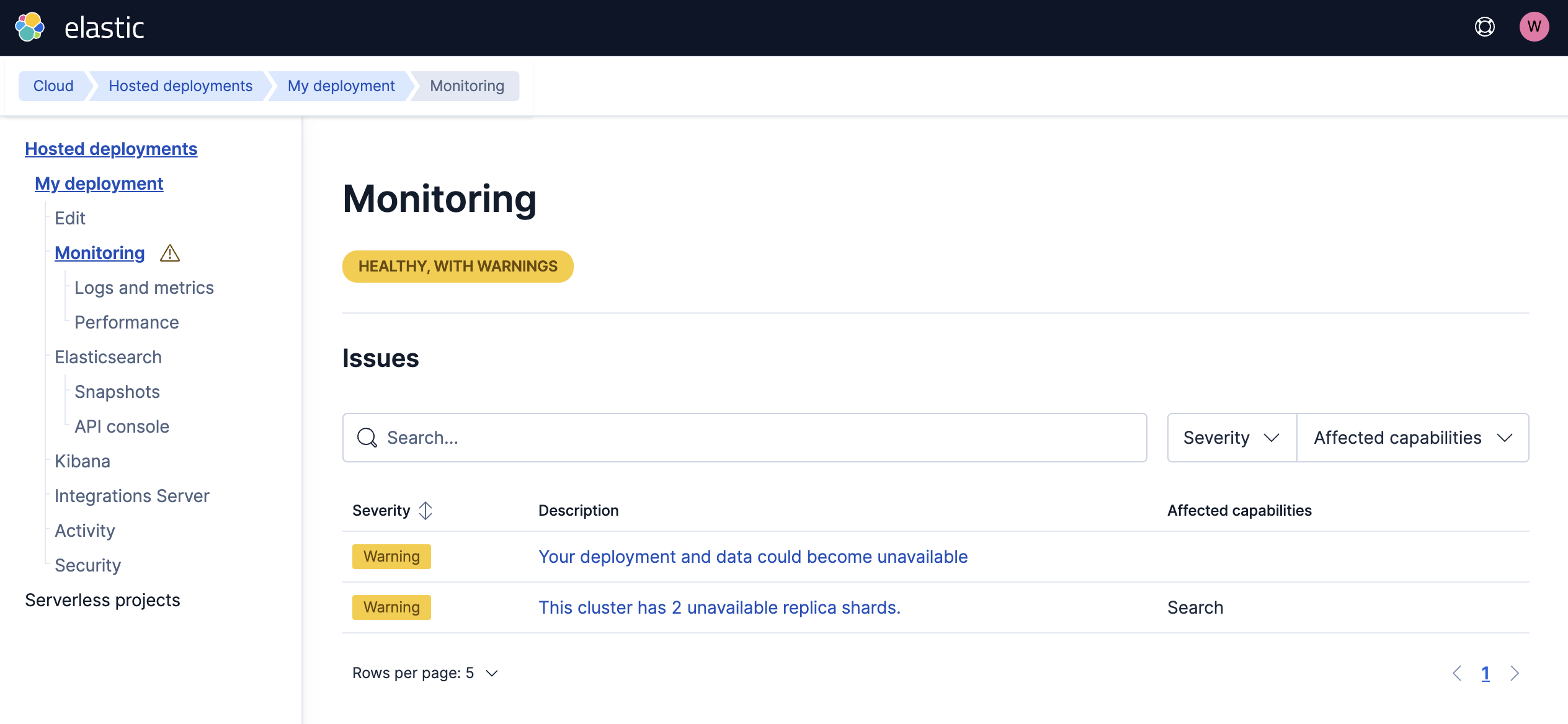
- Severity: A critical issue impacts operations such as search and ingest and should be addressed as soon as possible. Warnings don’t impact the cluster immediately but might lead to more critical issues over time such as a corrupted repository might lead to no backups being available in the future.
- Description: For most issues, you can click the description to get more details page on the specific issue and on how to fix it.
- Affected capabilities: Each of these areas might impact search, ingest, backups, or deployment management capabilities.
You can also search and filter the table based on affected resources, such as indices, repositories, nodes, or SLM policies. Individual issues can be further expanded to get more details and guided troubleshooting.
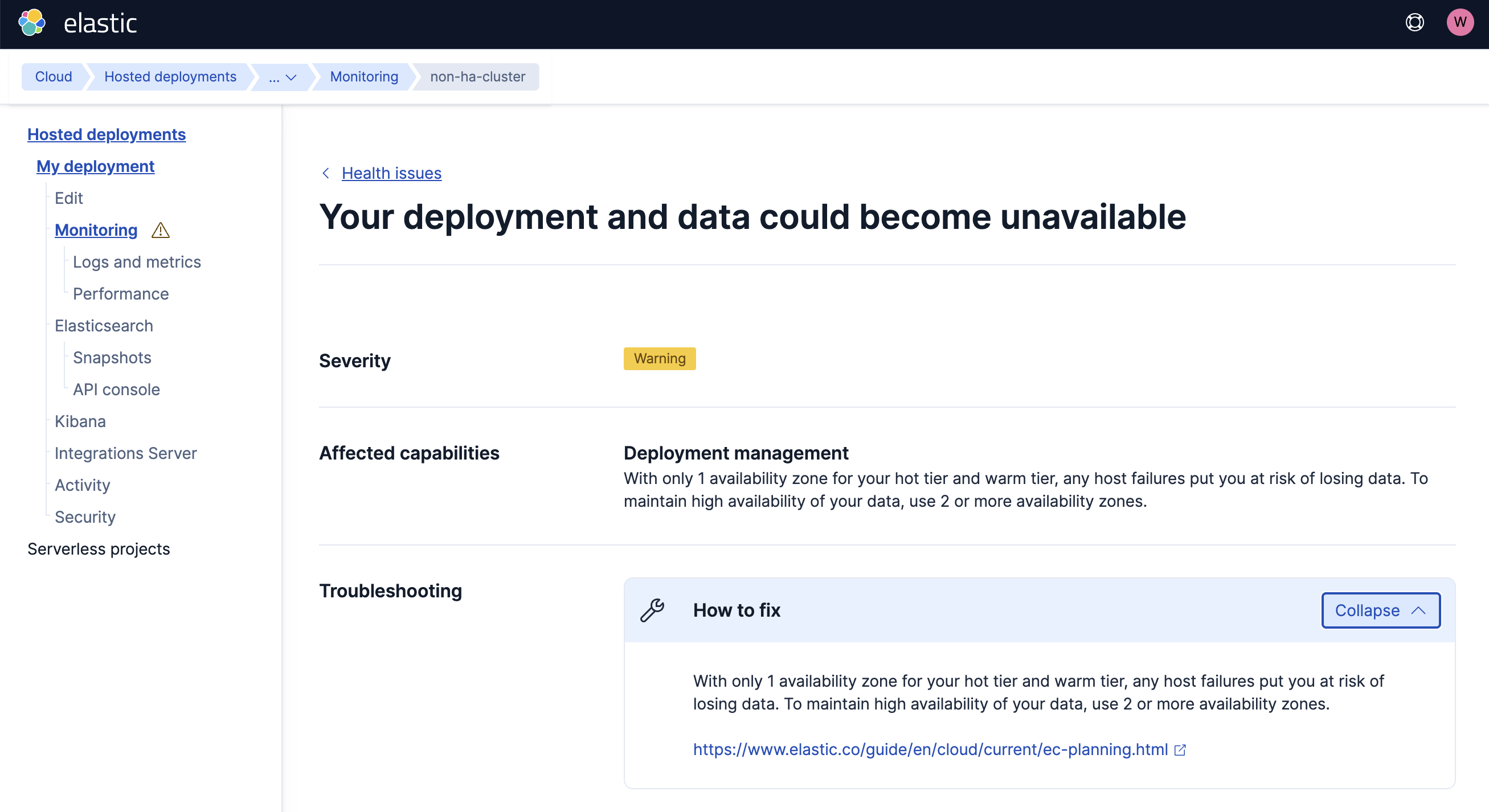
For more information about specific errors, refer to Troubleshoot Elasticsearch. You can also contact us if you need more help.
In the normal course of using your Elastic Cloud Hosted and Elastic Cloud Enterprise deployments, health warnings and errors might appear from time to time. Following are the most common scenarios and methods to resolve them.
| Category | Resolution |
|---|---|
| Health warning messages | Health warning messages will sometimes appear on the main page for one of your deployments, as well as on the Logs and metrics page. For Elastic Cloud Hosted deployments, these messages might reflect routine maintenance activity occurring on Elastic Cloud. |
| Configuration change failures | In more serious cases, your deployment may be unable to restart. The failure can be due to a variety of causes, the most frequent of these being invalid secure settings, expired plugins or bundles, or out of memory errors. The problem is often not detected until an attempt is made to restart the deployment following a routine configuration change, such as a deployment resizing. |
| Out of memory errors | Out of memory errors (OOMs) may occur during your deployment’s normal operations, and these can have a very negative impact on performance. Common causes of memory shortages are oversharding, data retention oversights, and the overall request volume. On your deployment page, you can check the JVM memory pressure indicator to get the current memory usage of each node of your deployment. You can also review the common causes of high JVM memory usage to help diagnose the source of unexpectedly high memory pressure levels. To learn more, refer to Troubleshoot high memory pressure. |
For clusters that suffer out-of-memory failures, it can be difficult to determine whether the clusters are in a completely healthy state afterwards. For this reason, Elastic Cloud Hosted automatically reboots clusters that suffer out-of-memory failures.
You will receive an email notification to let you know that a restart occurred. For repeated alerts, the emails are aggregated so that you do not receive an excessive number of notifications. Either resizing your cluster to reduce memory pressure or reducing the workload that a cluster is being asked to handle can help avoid these cluster restarts.
Elastic Cloud Hosted deployments offer an additional Performance page to get further information about your cluster performance.
If you observe issues on search and ingest operations in terms of increased latency or throughput for queries, these might not be directly reported on the Monitoring page, unless they are related to shard health or master node availability.
The Performance page and the out-of-the-box logs allow you to monitor your cluster performance, but for production applications we strongly recommend setting up a dedicated monitoring cluster. Refer to Understanding deployment health, for more guidelines on how to monitor you cluster performance.
Learn more about the performance page and the metrics it captures.
For Elastic Cloud Enterprise deployments, you can use platform monitoring to access preconfigured performance metrics.
Elastic Cloud Hosted and Elastic Cloud Enterprise also provide a JVM memory pressure indicator for each node in your cluster in your deployment overview. This indicator can help you to determine when you need to upgrade to a larger cluster.
Both Elastic Cloud Hosted and Elastic Cloud Enterprise offer out-of-the-box logs and metrics that you can access to get insight into your deployment's performance.
In a production environment, it’s important set up dedicated health monitoring using stack monitoring. Stack monitoring allows you to retain the logs and metrics that can be used to troubleshoot any health issues in your deployments. In the event of that you need to contact our support team, they can use the retained data to help diagnose any problems that you may encounter.
You have the option of sending logs and metrics to a separate, specialized monitoring deployment, which ensures that they’re available in the event of a deployment outage. The monitoring deployment also gives you access to Kibana stack monitoring features, through which you can view health and performance data for all of your deployment resources.
In a non-production Elastic Cloud Hosted environment, you may choose to rely on the logs and metrics that are available for your deployment by default. The deployment Logs and metrics page displays any current deployment health warnings, and from there you can also view standard log files from the last 24 hours.
The logs capture any activity related to your deployments, their component resources, snapshotting behavior, and more. You can use the search bar to filter the logs by, for example, a specific instance (instance-0000000005), a configuration file (roles.yml), an operation type (snapshot, autoscaling), or a component (kibana, ent-search).
In Elastic Cloud Enterprise, you can use platform monitoring to view deployment logs and metrics, as well as proxy logs. From your deployment page, select either the Elasticsearch, Kibana, and Integrations Server components, and use the external links to access each service's logs and metrics.
Elastic Cloud allows smaller instance sizes to get temporarily boosted vCPU when under heavy load. vCPU boosting is governed by vCPU credits that instances can earn over time when vCPU usage is less than the assigned amount.
You can check the Monitoring > Performance > CPU Credits section of the Elastic Cloud Console, and find the related metrics:
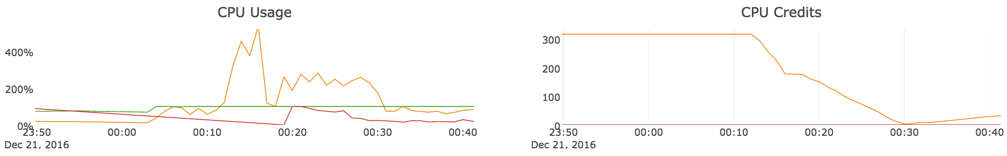
If you need your cluster to be able to sustain a certain level of performance, you can't rely on CPU boosting to handle the workload except temporarily. To ensure that performance can be sustained, consider increasing the size of your cluster. Refer to Troubleshoot performance degrading over time for more guidance.
We’ve compiled some guidelines to help you ensure the health of your deployments over time. These can help you to better understand the available performance metrics, and to make decisions involving performance and high availability.
- Diagnose unavailable nodes
- Learn about common symptoms and possible actions that you can take to resolve issues when one or more nodes become unhealthy or unavailable.
- Diagnose unavailable shards
- Provide instructions on how to troubleshoot issues related to unassigned shards.
- Troubleshoot performance degrading over time
- Address performance degradation on a smaller size Elasticsearch cluster.
- Troubleshoot cluster availability using performance metrics
- High availability involves more than setting multiple availability zones (although that’s really important!). Learn how to assess performance and workloads to determine if your deployment has adequate resources to mitigate a potential node failure.
- Troubleshoot high memory pressure
- Learn about typical memory usage patterns, how to assess when the deployment memory usage levels are problematic, how this impacts performance, and how to resolve memory-related issues.
- Troubleshoot slow cluster response time
- Learn about the common causes of increased query response times and decreased performance in your deployment.
- Understanding node moves and system maintenance
- Learn about why we may, from time to time, relocate your Elastic Cloud Hosted deployments across hosts.