User roles
ECE ECK Elastic Cloud Hosted Self Managed
After a user is authenticated, Elastic Stack needs to determine whether the user behind an incoming request is allowed to execute the request. The primary method of authorization in a cluster is role-based access control (RBAC), although Elastic Stack also supports Attribute-based access control (ABAC).
If you use Elastic Cloud Enterprise or Elastic Cloud Hosted, then you can also implement RBAC at the level of your Elastic Cloud Enterprise orchestrator or Elastic Cloud organization.
If you use Elastic Cloud Serverless, then you can only manage RBAC at the Elastic Cloud organization level.
You must authenticate users at the same level where you implement RBAC. For example, if you want to use organization-level roles, than you must authenticate your users at the organization level.
Role-based access control (RBAC) enables you to authorize users by assigning privileges to roles and assigning roles to users or groups. This is the primary way of controlling access to resources in Elastic Stack.
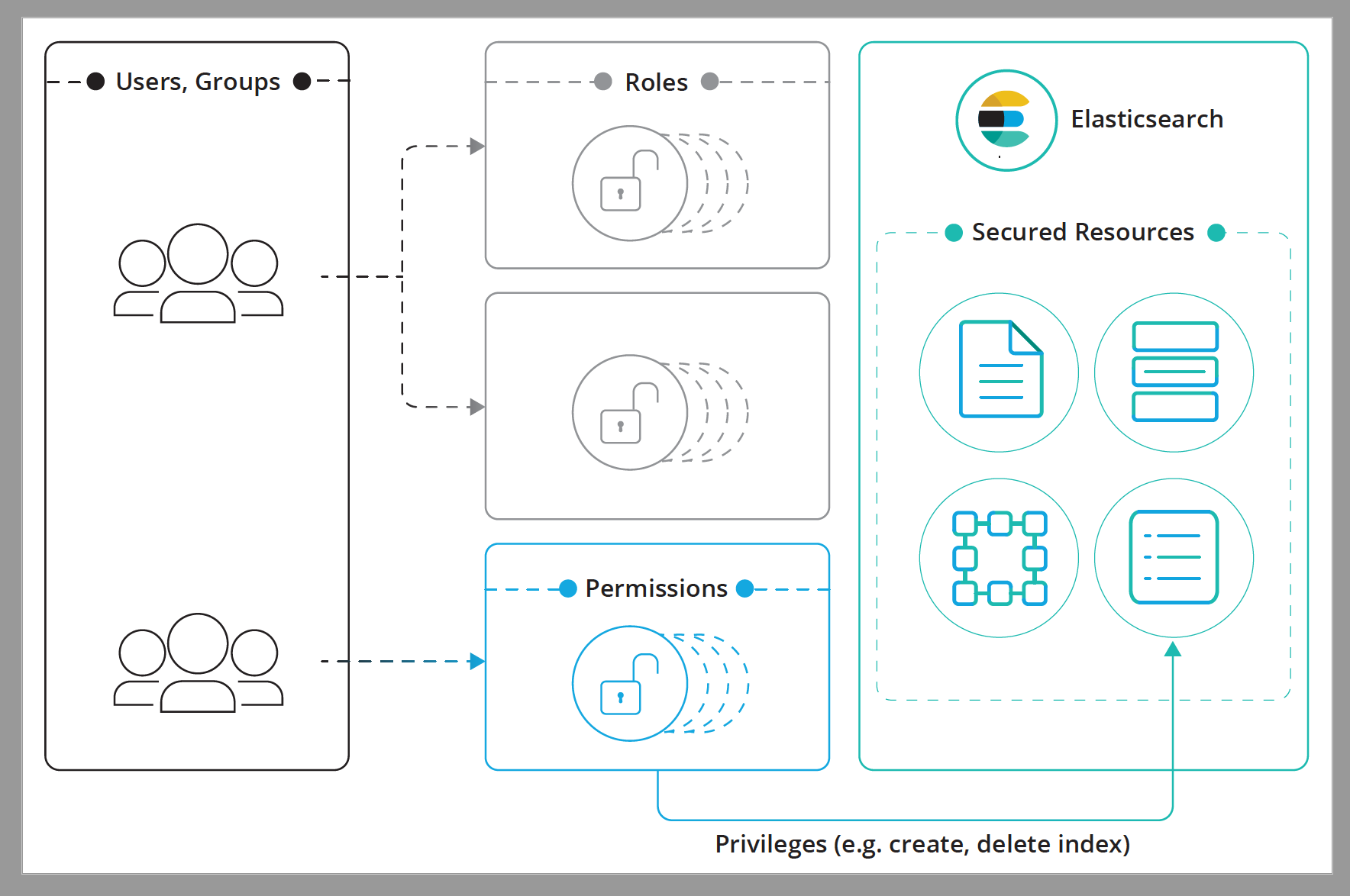
The authorization process revolves around the following constructs:
- Secured Resource
- A resource to which access is restricted. Indices, aliases, documents, fields, users, and the Elasticsearch cluster itself are all examples of secured objects.
- Privilege
- A named group of one or more actions that a user may execute against a secured resource. Each secured resource has its own sets of available privileges. For example,
readis an index privilege that represents all actions that enable reading the indexed/stored data. For a complete list of available privileges, see Elasticsearch privileges. - Permissions
-
A set of one or more privileges against a secured resource. Permissions can easily be described in words, here are few examples:
readprivilege on theproductsdata stream or indexmanageprivilege on the clusterrun_asprivilege onjohnuserreadprivilege on documents that match query Xreadprivilege oncredit_cardfield
- Role
- A named set of permissions
- User
- The authenticated user.
- Group
- One or more groups to which a user belongs. Groups are not supported in some realms, such as native, file, or PKI realms.
A role has a unique name and identifies a set of permissions that translate to privileges on resources. You can associate a user or group with an arbitrary number of roles. When you map roles to groups, the roles of a user in that group are the combination of the roles assigned to that group and the roles assigned to that user. Likewise, the total set of permissions that a user has is defined by the union of the permissions in all its roles.
Review these topics to learn how to configure RBAC in your cluster or deployment:
- Learn about built-in roles
- Define your own roles
- Learn about the Elasticsearch and Kibana privileges you can assign to roles
- Learn how to control access at the document and field level
The way that you assign roles to users depends on your authentication realm:
- Native realm:
- Using Elasticsearch API
_securityendpoints - In Kibana, using the Stack Management > Security > Users page
- Using Elasticsearch API
- File realm:
- Using a
user_rolesfile - In ECK: As part of a basic authentication secret
- Using a
- External realms: By mapping users and groups to roles
- Learn how to delegate authorization to another realm
- Learn how to build a custom authorization plugin for unsupported systems or advanced applications
- Learn how to submit requests on behalf of other users
- Learn about attribute-based access control
User roles are also used to control access to Kibana spaces.
Attribute-based access control (ABAC) enables you to use attributes to restrict access to documents in search queries and aggregations. For example, you can assign attributes to users and documents, then implement an access policy in a role definition. Users with that role can read a specific document only if they have all the required attributes.
For more information, see Document-level attribute-based access control with Elasticsearch.