Service-oriented architecture
Elastic Cloud Enterprise has a service-oriented architecture that lets you:
- Scale each service separately, with different reliability and performance requirements.
- Access services through the API.
- Deploy each service independently in its own Docker container.
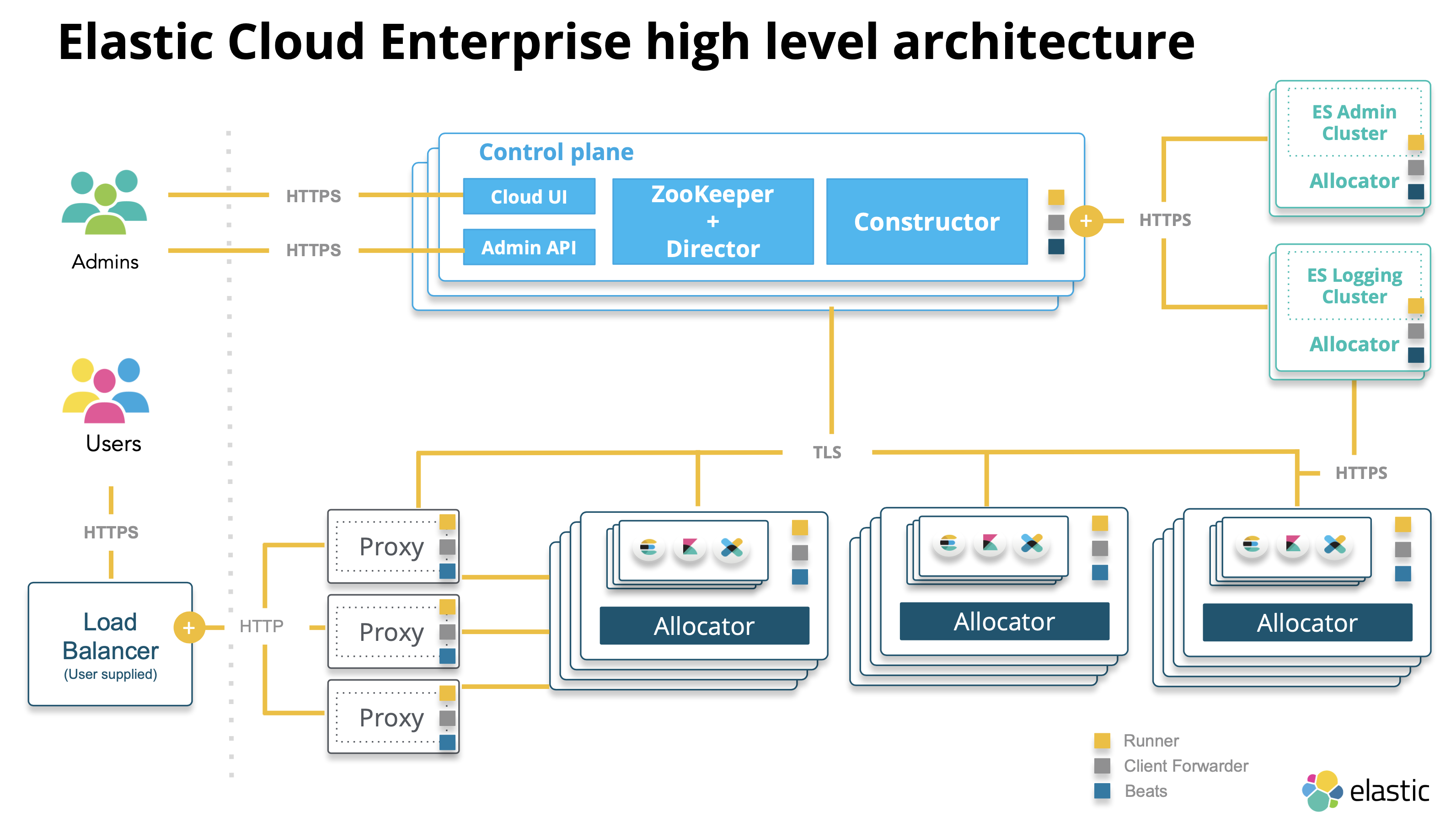
The control plane of ECE include the following management services:
ZooKeeper
- ZooKeeper is a distributed, strongly consistent data store.
- Holds essential information for ECE components: Proxy routing tables, memory capacity advertised by the allocators, changes committed through Admin Console, and so on.
- Acts as a message bus for communication between the services.
- Talks to ECE components using STunnel.
- Stores the state of the ECE installation and the state of all deployments running in ECE.
Director
- Manages the ZK data store and signs the CSRs (certificate signing requests) for internal clients that want to communicate with ZooKeeper.
- Maintains the stunnels used by ZooKeeper for communication and establishes quorum when new ZooKeeper nodes are created.
Constructor
- Works like a scheduler that monitors requests from the Admin console.
- Determines what needs to be changed, and writes the changes to ZooKeeper nodes monitored by the allocators.
- Assigns cluster nodes to allocators.
- Maximizes the utilization of underlying allocators to reduce the need to spin up extra hardware for new deployments.
- Places cluster nodes and instances within different availability zones to ensure that the deployment can survive any downtime of a whole zone. You can designate these availability zones when you install ECE.
Cloud UI and API
Provide web and API access for administrators to manage and monitor the ECE installation.
- Handle user requests, mapping deployment IDs that are passed in request URLs for the container to the actual Elasticsearch cluster nodes and other instances. The association of deployment IDs to a container is stored in ZooKeeper, cached by the proxies. In the event of ZooKeeper downtime, the platform can still service the requests to existing deployments by using the cache.
- Keep track of the state and availability of zones, if you have a highly available Elasticsearch cluster. If one of the zones goes down, the proxy will not route any requests there.
- Help with no-downtime scaling and upgrades. Before performing an upgrade, a snapshot is taken, and data is migrated to the new nodes. When the migration is complete, a proxy switches the traffic to the new nodes and disconnects the old ones.
- Multiple proxies are usually configured behind a load balancer to ensure that the system remains available.
Run on all the machines that host Elasticsearch nodes and Kibana instances.
Control the lifecycle of cluster nodes by:
- Creating new containers and starting Elasticsearch nodes when requested
- Restarting a node if it becomes unresponsive
- Removing a node if it is no longer needed
Advertise the memory capacity of the underlying host machine to ZooKeeper so that the Constructor can make an informed decision on where to deploy.