Redis module
Refer to the Elastic Integrations documentation.
Learn more
Elastic Agent is a single, unified way to add monitoring for logs, metrics, and other types of data to a host. It can also protect hosts from security threats, query data from operating systems, forward data from remote services or hardware, and more. Refer to the documentation for a detailed comparison of Beats and Elastic Agent.
The redis module parses logs and slowlogs created by Redis.
When you run the module, it performs a few tasks under the hood:
- Sets the default paths to the log files (but don’t worry, you can override the defaults)
- Makes sure each multiline log event gets sent as a single event
- Uses an Elasticsearch ingest pipeline to parse and process the log lines, shaping the data into a structure suitable for visualizing in Kibana
- Deploys dashboards for visualizing the log data
Read the quick start to learn how to configure and run modules.
The redis module has two filesets:
- The
logfileset collects and parses the logs that Redis writes to disk. - The
slowlogfileset connects to Redis via the network and retrieves the slow logs by using theSLOWLOGcommand.
For the log fileset, make sure the logfile option, from the Redis configuration file, is set to redis-server.log.
For the slowlog fileset, make sure the slowlog-log-slower-than option, from the Redis configuration file, is set to a lower value than the default one.
The Redis log fileset was tested with logs from Redis versions 1.2.6, 2.4.6, and 3.0.2, so we expect compatibility with any version 1.x, 2.x, or 3.x.
On Windows, the default paths assume that Redis was installed from the Chocolatey repository.
The Redis slowlog fileset was tested with Redis 3.0.2 and 2.4.6. We expect compatibility with any Redis version newer than 2.2.12, when the SLOWLOG command was added.
You can further refine the behavior of the redis module by specifying variable settings in the modules.d/redis.yml file, or overriding settings at the command line.
You must enable at least one fileset in the module. Filesets are disabled by default.
The following example shows how to set paths in the modules.d/redis.yml file to override the default paths for Redis logs. It also shows how to set the host and password to retrieve slow logs:
- module: redis
log:
enabled: true
var.paths: ["/path/to/log/redis/redis-server.log*"]
slowlog:
enabled: true
var.hosts: ["localhost:6378"]
var.password: "{pwd}"
To specify the same settings at the command line, you use:
-M "redis.log.var.paths=[/path/to/log/redis/redis-server.log*]" -M "redis.slowlog.var.hosts=[localhost:6378]" -M "redis.slowlog.var.password=[YOUR_PASSWORD]"
Each fileset has separate variable settings for configuring the behavior of the module. If you don’t specify variable settings, the redis module uses the defaults.
For advanced use cases, you can also override input settings. See Override input settings.
When you specify a setting at the command line, remember to prefix the setting with the module name, for example, redis.log.var.paths instead of log.var.paths.
var.paths- An array of glob-based paths that specify where to look for the log files. All patterns supported by Go Glob are also supported here. For example, you can use wildcards to fetch all files from a predefined level of subdirectories:
/path/to/log/*/*.log. This fetches all.logfiles from the subfolders of/path/to/log. It does not fetch log files from the/path/to/logfolder itself. If this setting is left empty, Filebeat will choose log paths based on your operating system.
var.hosts- An array of hosts to which Filebeat should connect to retrieve the slow logs. If left empty,
localhost:6379is assumed. var.password- The password to use to connect to Redis, in case Redis authentication is enabled (the
requirepassoption in the Redis configuration).
This module comes with a sample dashboard. For example:
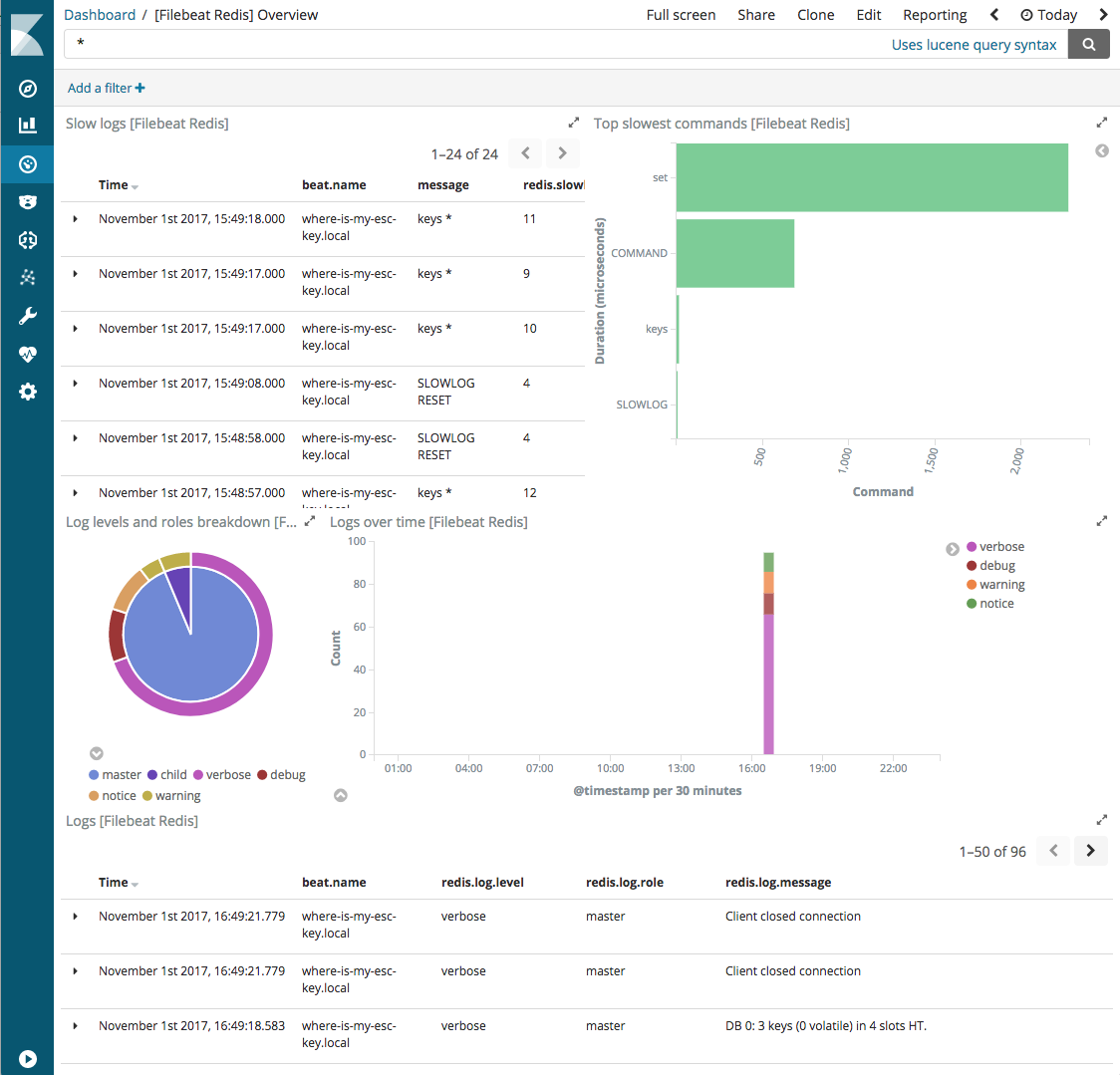
For a description of each field in the module, see the exported fields section.