Getting started
This page guides you through the installation process of the PHP client, shows you how to instantiate the client, and how to perform basic Elasticsearch operations with it.
If you don’t have composer you can install it by running the following commands:
curl -s http://getcomposer.org/installer | php
php composer.phar install
To install the latest version of the client, run the following command:
composer require elasticsearch/elasticsearch
When you have installed elasticsearch-php you can start using it with the Client class. You can use the ClientBuilder class to create this object:
require 'vendor/autoload.php';
$client = Elastic\Elasticsearch\ClientBuilder::create()->build();
Refer to the Installation page to learn more.
You can connect to the Elastic Cloud using an API key and the Elasticsearch endpoint.
$client = ClientBuilder::create()
->setHosts(['<elasticsearch-endpoint>'])
->setApiKey('<api-key>')
->build();
Your Elasticsearch endpoint can be found on the My deployment page of your deployment:
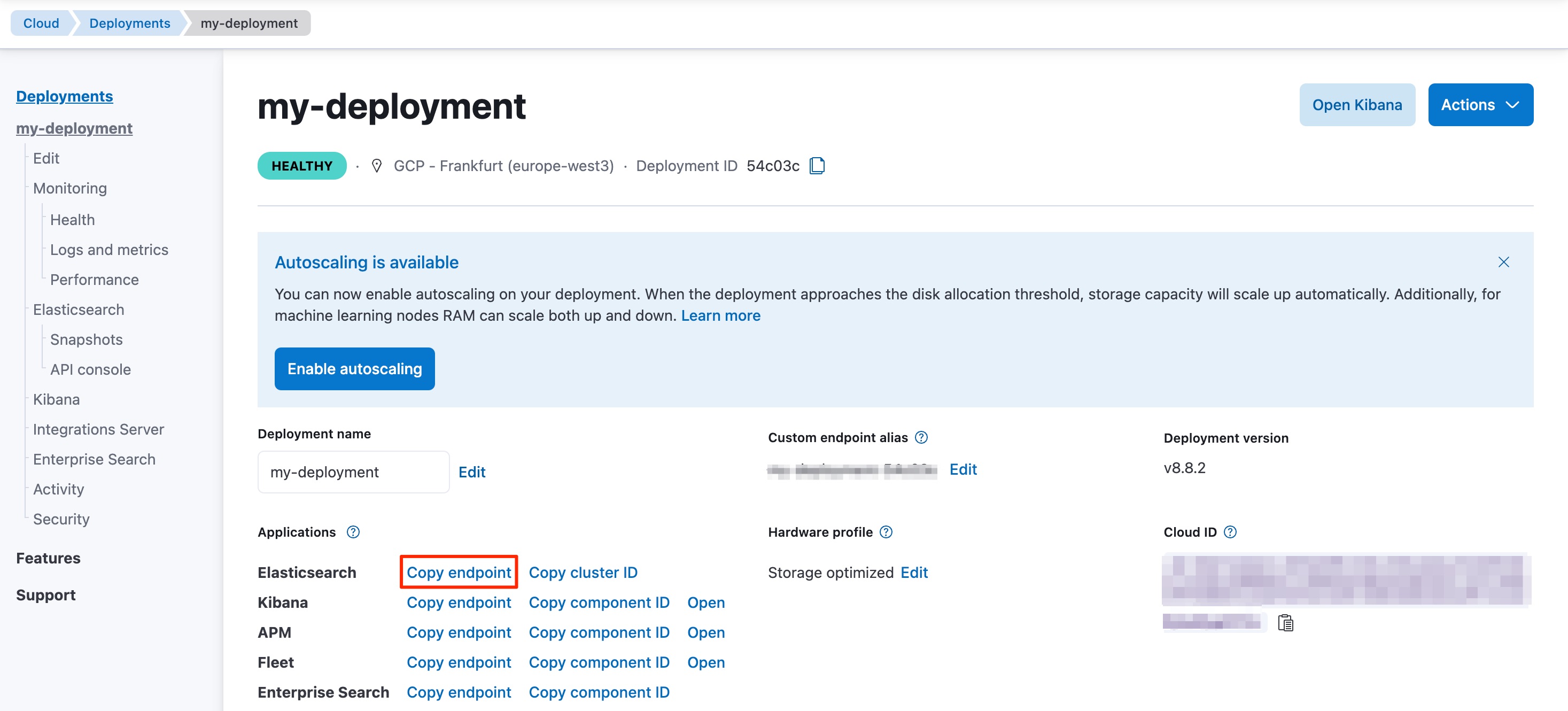
You can generate an API key on the Management page under Security.
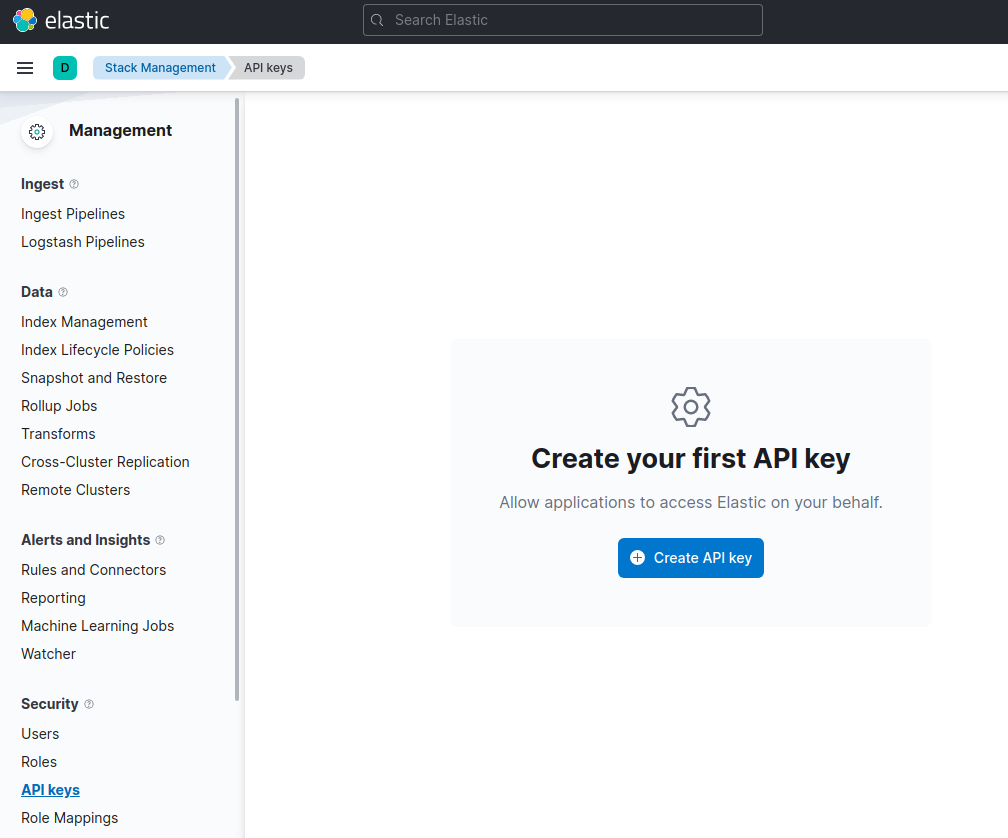
For other connection options, refer to the Connecting section.
Time to use Elasticsearch! This section walks you through the basic, and most important, operations of Elasticsearch. For more operations and more advanced examples, refer to the Operations page.
This is how you create the my_index index:
$client = ClientBuilder::create()->build();
$params = [
'index' => 'my_index'
];
// Create the index
$response = $client->indices()->create($params);
This is a simple way of indexing a document:
$params = [
'index' => 'my_index',
'body' => [ 'testField' => 'abc']
];
// Document will be indexed to my_index/_doc/<autogenerated ID>
$response = $client->index($params);
You can bulk index documents with batches in a slightly more complex way:
$params = ['body' => []];
for ($i = 1; $i <= 1234567; $i++) {
$params['body'][] = [
'index' => [
'_index' => 'my_index',
'_id' => $i
]
];
$params['body'][] = [
'my_field' => 'my_value',
'second_field' => 'some more values'
];
// Every 1000 documents stop and send the bulk request
if ($i % 1000 == 0) {
$responses = $client->bulk($params);
// erase the old bulk request
$params = ['body' => []];
// unset the bulk response when you are done to save memory
unset($responses);
}
}
// Send the last batch if it exists
if (!empty($params['body'])) {
$responses = $client->bulk($params);
}
You can get documents by using the following code:
$params = [
'index' => 'my_index',
'id' => 'my_id'
];
// Get doc at /my_index/_doc/my_id
$response = $client->get($params);
This is how you can create a single match query with the PHP client:
$params = [
'index' => 'my_index',
'body' => [
'query' => [
'match' => [
'testField' => 'abc'
]
]
]
];
$results = $client->search($params);
This is how you can update a document, for example to add a new field:
$params = [
'index' => 'my_index',
'id' => 'my_id',
'body' => [
'doc' => [
'new_field' => 'abc'
]
]
];
// Update doc at /my_index/_doc/my_id
$response = $client->update($params);
$params = [
'index' => 'my_index',
'id' => 'my_id'
];
// Delete doc at /my_index/_doc_/my_id
$response = $client->delete($params);
$params = ['index' => 'my_index'];
$response = $client->indices()->delete($params);
- Use Client helpers for a more confortable experience with the APIs.